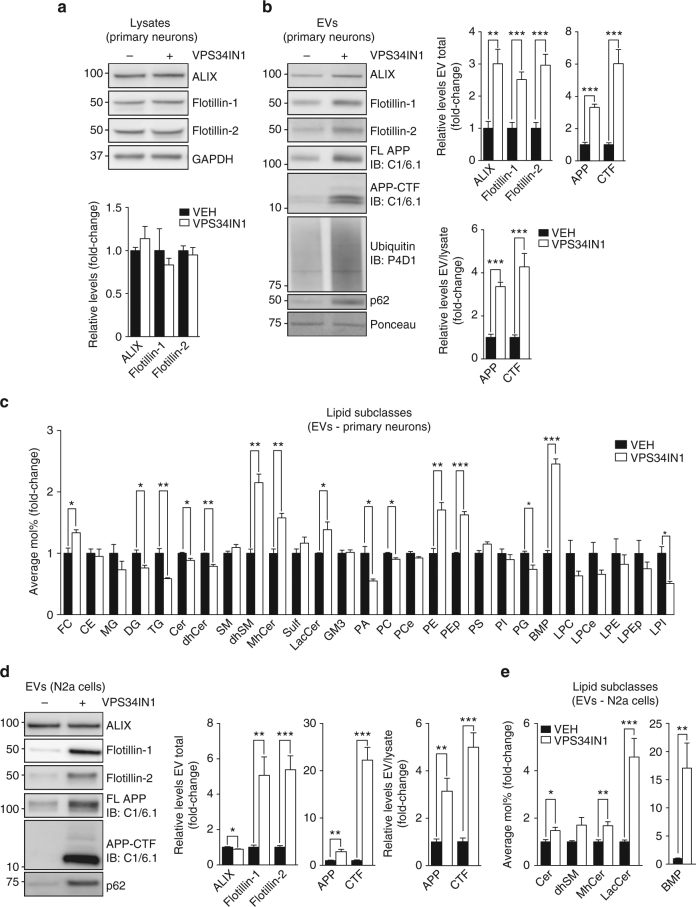
Fig. 4.
VPS34IN1 treatment causes secretion of extracellular vesicles (EVs) enriched for APP-CTFs, sphingolipids and BMP. a, b Western blot analysis of cell lysates and EVs from primary cortical neurons treated with vehicle or VPS34IN1 at 3 µM for 24 h. EV protein levels were normalized to lysate total protein (EV total) or lysate levels of the corresponding protein (EV/Lysate ratio). Bar graph denotes average protein levels normalized to vehicle (mean ± SEM, N = 4 for cell lysates, N = 6 for EVs, from two independent experiments). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 in two-tailed Student’s t test. c LC–MS analysis of lipids extracted from EVs collected from primary cortical neuron culture media after treatment as in a. Values are expressed as average Mol% of total lipid measured, normalized to vehicle (mean ± SEM, N = 3, each from a pool of two biological replicates). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.01 in two-tailed Student’s t test. d, e Western blot and LC–MS analysis of lipids extracted from EVs collected from N2a cell culture media after treatment with vehicle or VPS34IN1 at 1 µM for 24 h. EV protein levels were normalized to lysate total protein (EV total) or lysate levels of the corresponding protein (EV/Lysate ratio). For complete lipid panel, see Supplementary Fig. 6d (mean ± SEM, N = 6, from two independent experiments). Lipid values are expressed as average Mol% of total lipids measured, normalized to vehicle (mean ± SEM N = 7, each from a pool of two biological replicates) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 in two-tailed Student’s t test