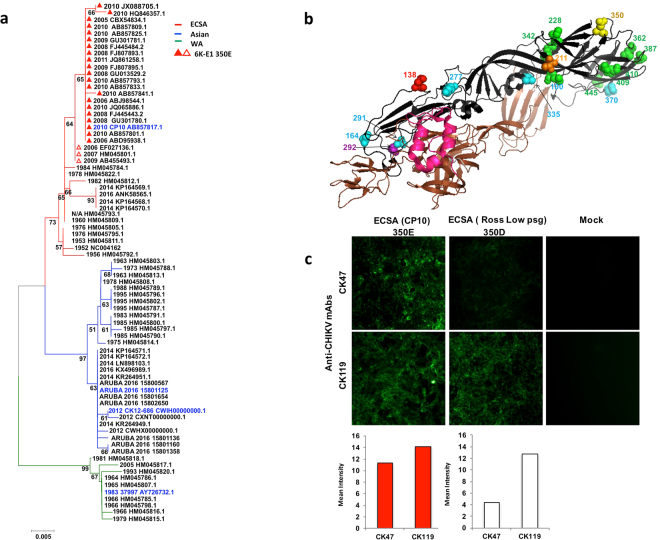
Figure 3.
Amino acid variation at position 350 of the CHIKV 6K-E1 protein. (a) Nearest-neighbor-joining tree with 1,000 bootstraps of sequences from the indicated CHIKV strains was constructed using MEGA version 7 (Kumar, Stecher, and Tamura 2015). Scale bar denotes the genetic distance; numbers below the branches represent percentage of associated taxa clustered together. The three major genotype branches are shown in different colors: ECSA (red), Asian (blue), and WA (green). Collection year and Genbank accession number of each sequence is shown. Red triangles indicate CHIKV strains with glutamic acid (E) at position 350 of the 6K-E1 protein. Among those strains, closed or open triangles indicate valine (V) or alanine (A) (respectively) at amino acid position 292. CHIKV strains without a triangle possess aspartic acid (D) and “A” at positions 350 and 292, respectively. CHIKV strains used in plasmid construction and ARUBA-15801125 are indicated by blue. (b) 3D-structure of CHIKV glycoproteins based on Protein Data Bank number 3N42 using The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8 Schrödinger, LLC. E3 is shown in magenta, E2 in brown, and E1 in black. Spheres on E1 indicate amino acid positions that vary among the three genotypes of CHIKV. Purple and yellow spheres indicate amino acids at position 292 and 350, respectively. Red, green, and light-blue spheres indicate the ECSA-, WA- and Asian-genotype-specific amino acid residues, respectively. Orange spheres indicate amino acid positions that differ among all three genotypes. (c) Indirect immunofluorescence test of mAb labeling of CHIKV-infected cells. CP10 (350E), Ross Low psg strain (350D), or mock-infected Vero cells were stained with CK47 and CK119; labeling was detected with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody. Images are representative of results obtained from two independent experiments and were taken under 10X objective magnification. Red and white bars are fluorescent signal levels of 350E and 350D, respectively.