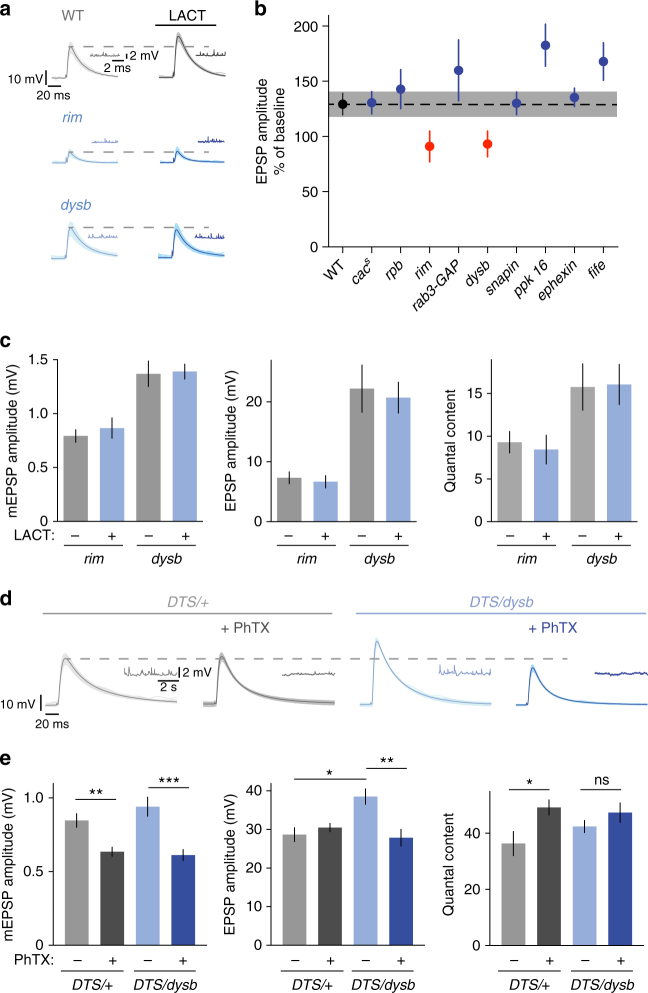
Fig. 7.
rim and dysbindin are required for proteasome-dependent potentiation. a Application of 100 µM lactacystin for 15 min to wild-type synapses and selected PHP mutants. Representative EPSP and mEPSP traces are shown for wild type, rim and dysbindin mutants. b For quantification, EPSP amplitude after lactacystin application was normalized to the EPSP amplitude at baseline. Wild-type EPSPs show an increase to 130% upon lactacystin treatment. The PHP mutants cacs, rim-binding protein (rbp), rab3-GAP, snapin (presynaptic RNAi), pickpocket16 (ppk 16), ephexin and fife show similar or stronger increases, whereas rim and dysbindin (dysb) mutants do not respond to lactacystin treatment. Due to defects in baseline EPSP amplitude in some of the genotypes, different [Ca2+]e concentrations were used to adjust baseline EPSP amplitudes to comparable values: WT: 0.3 mM; cacs: 0.5 mM; rbp: 1 mM; rim: 0.3 mM; rab3-GAP: 0.3 mM; dysbindin: 0.3 mM; snapin RNAi: 0.3 mM; pickpocket 16: 0.25 mM; ephexin: 0.25 mM; fife: 0.3 mM. Mean ± s.e.m.; n ≥ 8 cells. c Quantification of mEPSP amplitude, EPSP amplitude and quantal content of rim and dysbindin mutant synapses at baseline and after lactacystin application (100 µM for 15 min). Mean ± s.e.m.; n ≥ 10 cells. d Synapses expressing one allele of the mutant proteasome subunit presynaptically either in a wild-type background (DTS/+; het) or in larvae mutant for one allele of dysbindin (DTS/dysb; double het) were measured under baseline conditions and after application of 20 µM PhTX for 10 min (0.3 mM [Ca2+]e). Representative EPSP and mEPSP traces are shown. e Quantification of mEPSP amplitude, EPSP amplitude and quantal content for the experiment described in (d). DTS/+heterozygous synapses have no defect in PHP, whereas DTS/dysb double heterozygous synapses show no increase in quantal content after PhTX application. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001