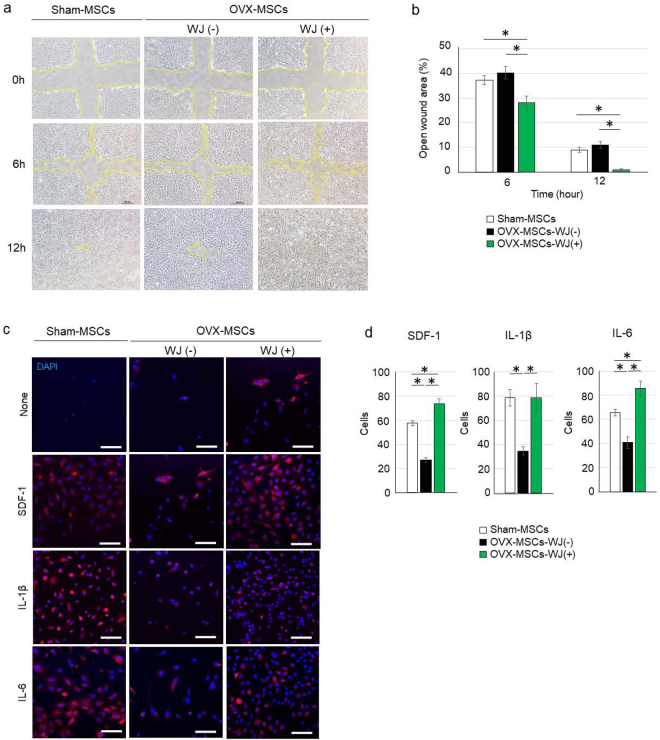
Figure 3.
Activating effects of WJS on migration capacity of OVX-MSCs. (a) Wound assay of Sham-MSCs, OVX-MSCs-WJ(-), and OVX-MSCs-WJ(+). *P < 0.05. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of 4 BM-MSC cultures. The open wound area was measured at 6 h and 12 h after performing the cross-scratch. Yellow lines indicate the boundary of cell migration. (b) The ratio of open wound area at 6 h and 12 h compared with 0 h. Six cross-scratch points in each BM-MSC culture were measured. *P < 0.05. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of 4 BM-MSC cultures. (c) Chemotaxis assay of Sham-MSCs, OVX-MSCs-WJ(-), and OVX-MSCs-WJ(+). BM-MSCs induced to migrate to the opposite side of the membrane by SDF-1, IL-1β, and IL-6 as observed by confocal microscope. DAPI was used for counterstaining nuclei (blue). Bar: 100 μm. SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor 1; IL-1β, interleukin-1 beta; IL-6, interleukin-6. (d) Numbers of BM-MSCs migrated to the opposite side of the membrane were counted in three fields of view for each BM-MSC type. *P < 0.05. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of 3 BM-MSC cultures.