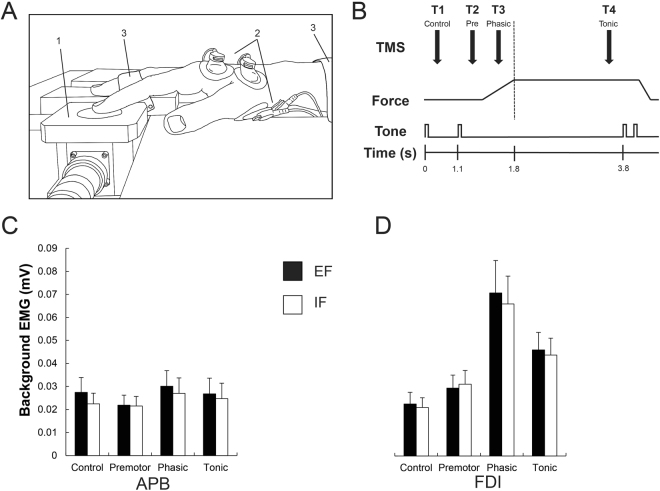
Figure 1.
(A) Experimental setup. The tip of the right index finger is resting on the force transducer (1). Two pairs of surface electrodes were placed over the (2) APB and FDI. The right forearm, middle, ring and pinky fingers were fixed by straps in order to minimize movements (3). (B) Time course of the task. Shown are the transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) time points, the force produced and the acoustic tones. Brain stimuli were applied during a resting or control phase (T1; 500 ms after the first tone), during the premotor phase (T2; between 100 and 200 ms after the second tone), the phasic phase (T3; between 300 and 600 ms after the second tone) and the tonic phase (T4; 2700 ms after the second tone). (C,D) Shown are the background EMG levels, obtained in a 50 ms time window before the brain stimulation, for the surrounding muscle APB (C) and the prime mover FDI (D) in all four different phases (control, premotor, phasic and tonic). There was a significant main effect of phase in the prime mover FDI, reflecting its activation during the motor task and no significant modulation of background EMG was found in the surrounding muscle APB. Black bars represent the external (EF) and the whites ones the internal focus of attention (IF).