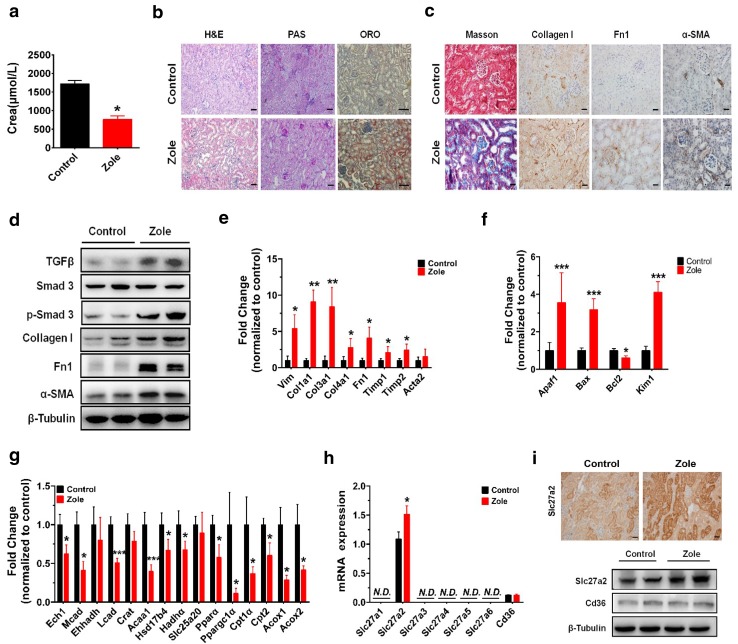
Fig. 4.
Effects of renal toxicity of zoledronate treatment in mice and its relative molecular pathways. a Reduced creatinine secretion in zoledronate-treated mice as compared with the control group. b Representative images of zoledronate untreated and treated mouse kidney sections stained with H&E, PAS and ORO staining (scale bar 1 mm). c Representative pictures of Masson’s trichrome staining (scale bar 50 μm) and collagen I, Fn1 and α-SMA IHC (scale bar 20 μm) for detection of zoledronate-induced kidney injury. d Western blot analysis of TGFβ1/Smad3 pathway and fibrosis markers in the kidney of controlled and zoledronate-treated mice. e Relative transcript levels of fibrosis and kidney-injury-related genes in controls and zoledronate-treated mice. f Relative mRNA levels of typical apoptosis and kidney injury factors. g Relative mRNA levels of FAO-related genes in controls and zoledronate-treated ones. h Relative transcript levels of FA uptake-related transporter or carrier in controls and zoledronate-treated ones. i Representative IHC images and western blot analysis of mouse kidney from control and zoledronate-treated mice for Slc27a2. (scale bar 20 μm). Each group had five mice and was treated for 4 weeks in the animal studies