Fig. 3.
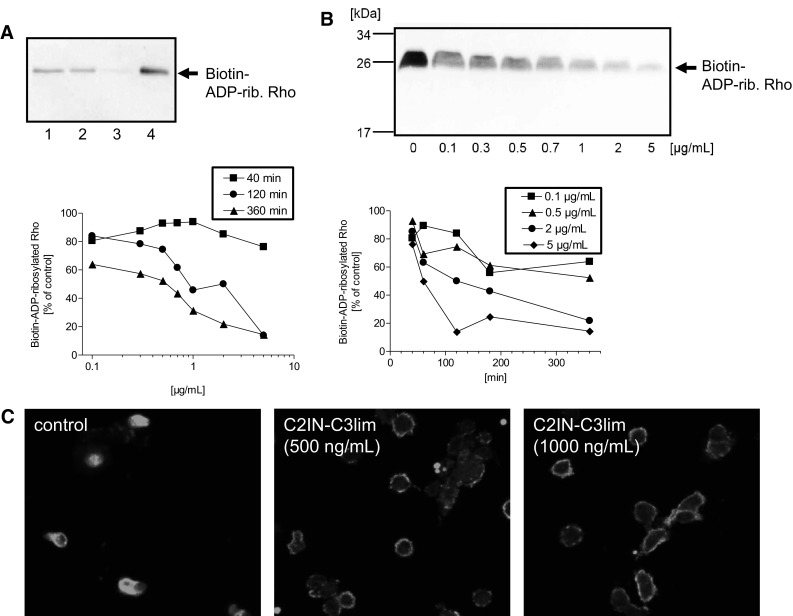
C2IN-C3lim ADP-ribosylates Rho and thereby rearranges the actin cytoskeleton in primary human monocytes ex vivo. a Primary human monocytes were isolated from healthy donors and incubated ex vivo in medium for 3 h at 37 °C with 500 ng/mL C2IN-C3lim (lane 1), 1 µg/mL C2IN-C3lim (lane 2), C2IN-C3lim (500 ng/mL) + C2IIa (1 µg/mL) (lane 3) or without toxin for control (lane 4). The cells were lysed and the ADP-ribosylation status of Rho from these cells (2.8 × 105 cells per sample) analyzed by sequential ADP-ribosylation with biotin-NAD+ as co-substrate and Western blotting. Note: A strong signal of biotin-ADP-ribosylated Rho in the Western blot indicates that Rho was not ADP-ribosylated in the intact cells while a weak signal of biotin-ADP-ribosylated Rho means that most of the Rho was already ADP-ribosylated in the living cells during incubation with the respective toxin, and therefore did not serve as substrate for the subsequent in vitro ADP-ribosylation reaction. b Concentration- and time-dependent effects of C2IN-C3lim on primary human monocytes. Analysis of the ADP-ribosylation status of Rho from monocytes, which were incubated for different times with increasing concentrations of C2IN-C3lim in the medium. The ADP-ribosylation status of Rho from the cells (4 × 105 cells per sample) was analyzed as described before and the Western blot shows the result for the 6 h incubation period. For comparison of the samples, the intensity of biotin-labeled Rho was evaluated via densitometry. The graphs show the intensity of biotin-ADP-ribosylated Rho, which corresponds to the amount of cellular Rho that was not ADP-ribosylated in the living cells during the incubation with C2IN-C3lim. c Primary human monocytes were isolated from healthy donors and incubated at 37 °C for 3 h in the presence of C2IN-C3lim (500 ng/mL or 1000 ng/mL). For control, cells were left untreated. Cells were fixed and actin stained with an antibody against ß-actin. The stained actin was visualized by confocal fluorescence microscopy
