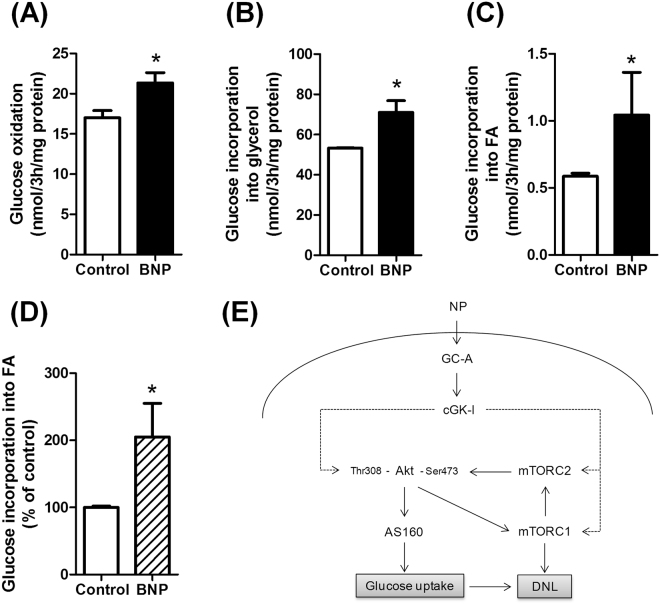
Figure 6.
Natriuretic peptides enhance glucose metabolism in human adipocytes. Effect of acute BNP 100 nM treatment on glucose oxidation (A), glucose incorporation into glycerol (B), and glucose incorporation into fatty acids (FA) (C) in hMADS adipocytes. (D) Effect of 100 nM BNP on glucose incorporation into FA in human isolated adipocytes. *p < 0.05 vs. control (n = 4–7). (E) Schematic model of NP-mediated glucose uptake in human adipocytes. Natriuretic peptides (NP) bind to a transmembrane receptor bearing a guanylyl cyclase activity called GC-A. Binding of NP to GC-A induces the production of cGMP and activation of cGK-I which activate Akt and mTORC2. Activation of mTORC2 phosphorylates Akt at Ser473 and enhances downstream signalling to the Rab-GTPase AS160 which promotes membrane GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake. NP therefore promote glucose uptake and enhance glucose incorporation into glycerol and FA pools through de novo lipogenesis.