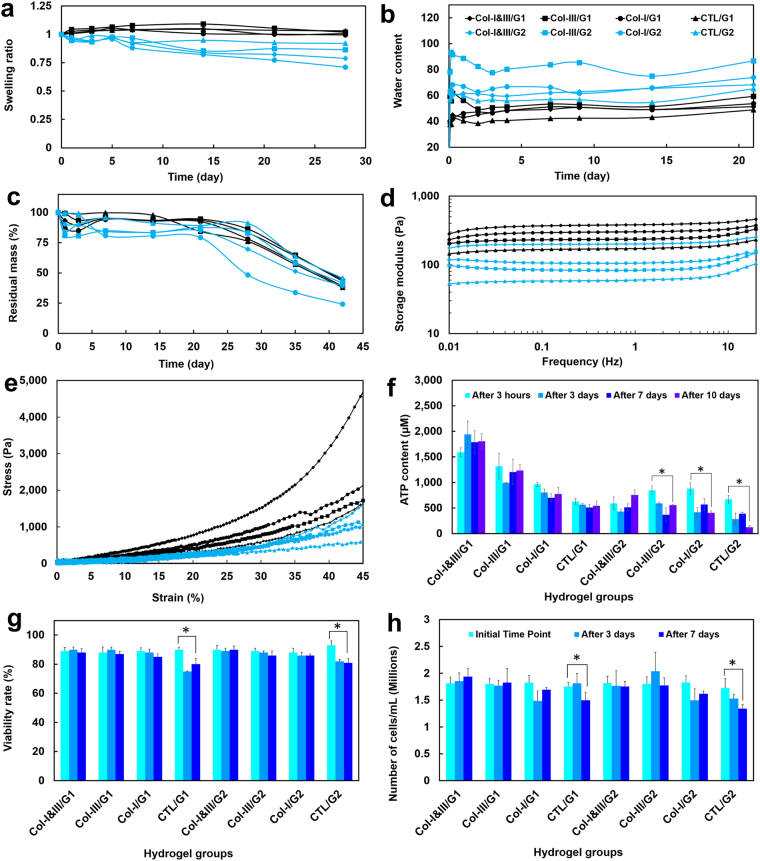
Figure 4.
(a) Swelling kinetic of the collagen (Col)/glycol-chitosan (GCS) hydrogels initiated from the wet state. Greater swelling ratios were obtained for the Col/GCS hydrogels with higher GCS concentrations (G1s). Wt and W0 are the wet weights at the arbitrary and initial times, respectively; (b) Water content of the hydrogels initiated from the dried state. Wt and Wd are the weights at the swollen and dried states, respectively. A sudden increase was found in the water content of the hydrogels 2 hours after immersion in PBS. The hydrogels reached an equilibrium water content after 2 days; (c) The fractional residual mass (%) of the hydrogels immersed in the enzyme solution for a duration of 42 days. A half-life of more than 35 days was found for the proposed hydrogels; (d) Average storage moduli of the hydrogels for the frequencies between 0.01 and 20 Hz. Larger storage moduli were found for the Col/GCS hydrogels compared with the associated negative controls; (e) Stress-strain curves of the hydrogels obtained through compression test. The area inscribed below the graph denotes the compressive toughness of the sample; (f) The adenosine triphosphate (ATP) content of the cells over a duration of 10 days; and (g,h) Cell viability rates (%) and cell density (total number of cells per mL) in each hydrogel configuration over a duration of 7 days (Col-III: collagen type III, Col-I: collagen type I, Col-I&III: both Col-I and Col-III, and CTL: negative controls. G1 and G2 represent the final GCS concentration of 2% and 1%, respectively).