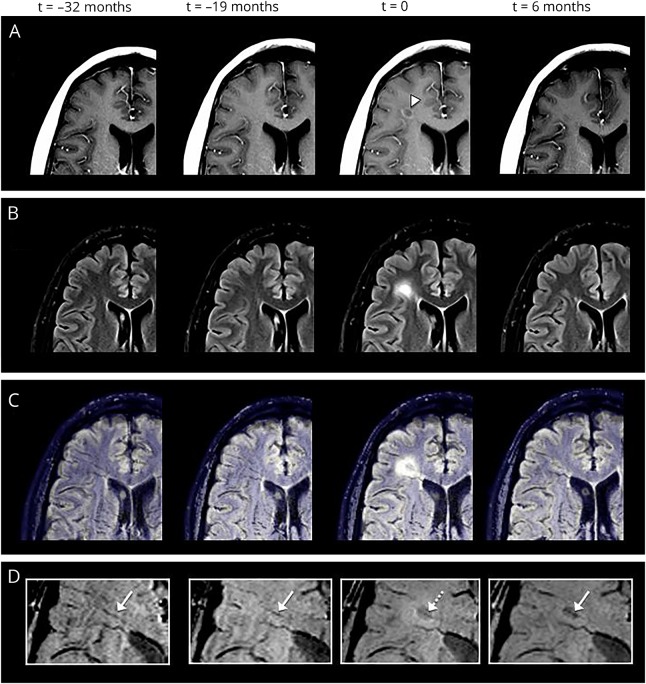
Figure 2. Example of venous narrowing.
Exemplary serial MRI examinations in a 34-year-old man with relapsing-remitting MS (disease duration at the time of acute contrast enhancement: 4 years, Expanded Disability Status Scale score: 2.5). (A) Postcontrast T1-weighted images demonstrate an acute contrast-enhancing lesion (t = 0; white arrowhead). (B) The lesion is prominently hyperintense on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images. Coregistered FLAIR-/susceptibility-weighted images (SWIs) (C) and magnified SWIs (D) demonstrate the central vein (dotted arrow; t = 0). At the time of contrast enhancement (t = 0), the venous diameter is significantly smaller (0.85 mm) compared with the MRI examination before contrast enhancement (t = −19 months; venous diameter: 1.3 mm) and after contrast enhancement (t = +6 months; venous diameter: 1.0 mm; white arrows).