Figure 5.
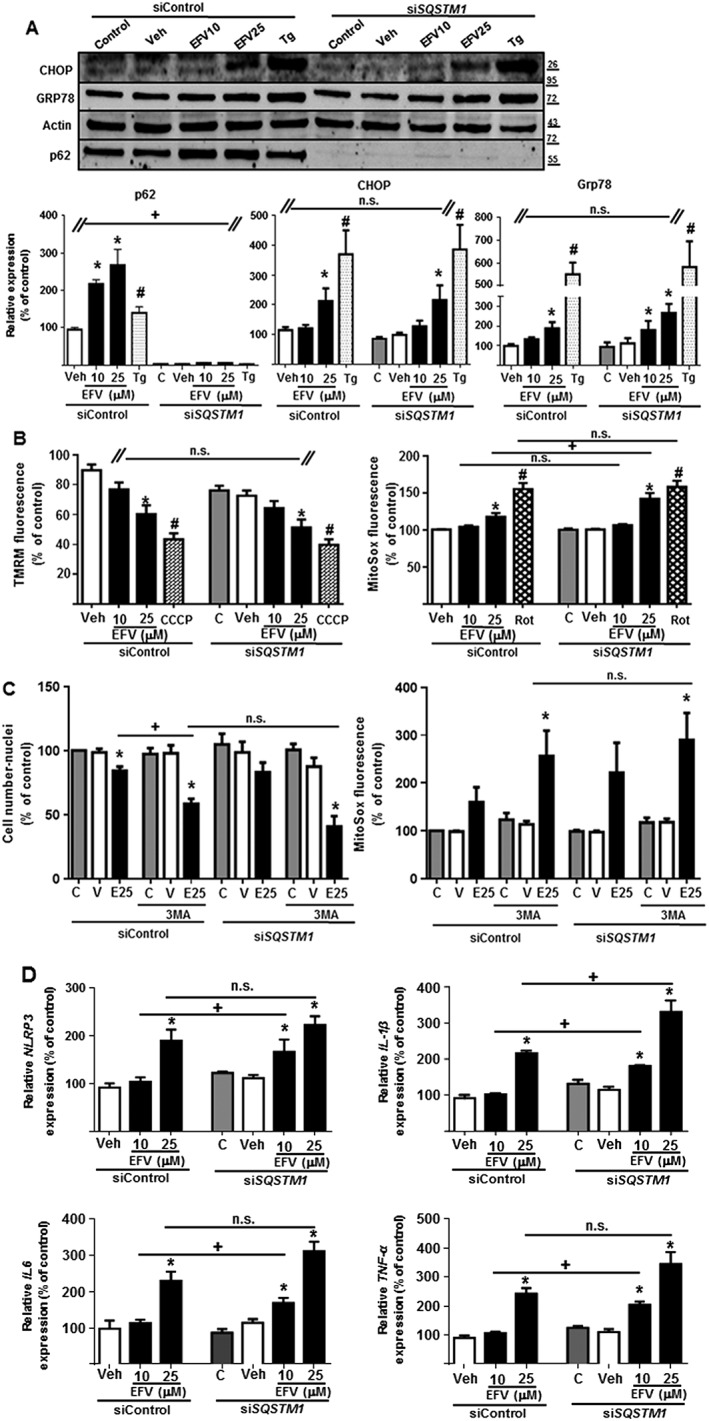
SQSTM1 silencing enhanced the mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammatory response induced by efavirenz but not the UPR. Hep3B cells transiently transfected with siControl or SQSTM1 were treated for 24 h with increasing concentrations of efavirenz (EFV), vehicle, thapsigargin (Tg) 2 μM, rotenone (Rot) 25 μM or CCCP 10 μM, in the absence or presence of the autophagic inhibitor 3MA. (A) Representative Western blot image of p62, CHOP and GRP78 and summary of densitometry data (n = 5). The absence of p62 confirmed the efficacy of SQSTM1 silencing. (B) Quantitative analysis of ΔΨm (tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester fluorescence) and mitochondrial superoxide production (MitoSOX fluorescence) by live cell fluorescence microscopy coupled with static cytometry (n = 7). (C) Quantitative analysis of the cell number (Hoechst fluorescence) and the mitochondrial superoxide production (MitoSOX fluorescence) by live cell fluorescence microscopy coupled with static cytometry. (D) Relative mRNA expression levels of inflammation‐related genes were analysed by quantitative RT‐PCR (n = 5). Data (mean ± SEM) were calculated as percentage of control (untreated SiControl cells). *P < 0.05, for efavirenz and #P < 0.05 for thapsigargin, rotenone or CCCP, significantly different from vehicle; one‐way ANOVA followed by a Newman–Keuls test. +P < 0.05, significantly different as indicated; Student's t‐test.
