Table 3.
Toxicity profile of some cholinium‐based ILs
| Anion | Biosystem | Comment on toxicity |
|---|---|---|
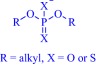
|
Eukaryotic cell: J774 murine macrophage | More toxic than NaCl.37 |
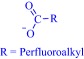
|
Eukaryotic cell: human lung fibroblast, human liver carcinoma cells, and human kidney fibroblast | Toxicity depends on the anion.27 |
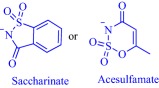
|
Multicellular organism: Daphnia magna | Less toxic than imidazolium and pyridinium ILs.38 |
|
|
Eukaryotic cell: Penicillium brevicompactum, P. glandicola, P. corylophilum, P. diversum | Could be more toxic than ethanol with toxicity depending on length and branching of alkyl chain.25 |
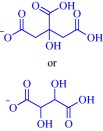
|
Prokaryotic cell: V. fischeri | More toxic than atrazine, benzene, 1‐butylpyridinium, 1‐butyl‐3‐methylimidazolium, and 1‐butyl‐1‐methylpyrrolidinium‐based ILs.33 |
|
|
Eukaryotic cell: human colon carcinoma Caco‐2 and hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells | No toxicity from cholinium cation. 34 |
|
Eukaryotic cell: channel catfish ovary cells. | Very low toxicity with EC50 > 1,000 mg L−1.44 |
