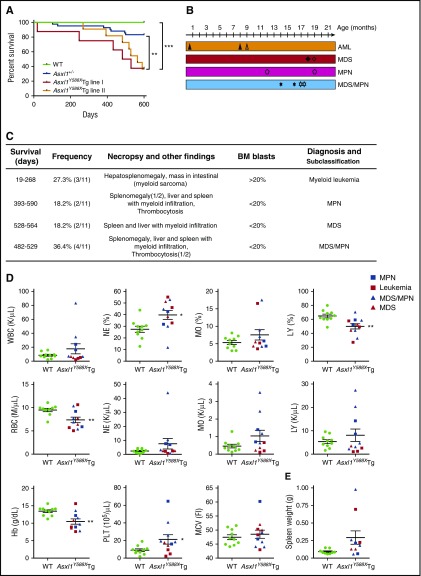
Figure 2.
Transgenic ASXL1aa1-587expression leads to myeloid malignancies in mice. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of the Asxl1Y588XTg line I (n = 8), Asxl1Y588XTg line II (n = 11), Asxl1+/− (n = 42), and WT mice (n = 20). ***P < .0001, **P < .01. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to assess statistical significance. (B) Timeline of mice developing myeloid malignancies. Solid shapes are mice from line I; the hollow shapes are from line II. (C) Diagnosis and subclassification of the myeloid malignancies developed in 11 aged Asxl1Y588XTg mice. (D) Peripheral blood counts of white blood cell (WBC; P = .242), percent of neutrophils (*P = .017), percent of monocytes (P = .1959), percent of lymphocytes (**P = .005), RBC (**P = .007), neutrophils (P = .2055), monocytes (P = .1174), lymphocytes (P = .3606), hemoglobin (**P = .004), platelets (*P = .048), and mean corpuscular volume (P = .5452) in Asxl1Y588XTg (n = 11) and WT mice (n = 10). (E) Spleen weight of Asxl1Y588XTg and WT mice (WT, n = 8; Asxl1Y588X, n = 9; P = .0643). Blue square, MPN; red square, leukemia; blue triangle, MDS/MPN; red triangle, MDS. *P < .05, **P < .01. Error bars represent mean ± SEM; unpaired t test was used to assess statistical significance.