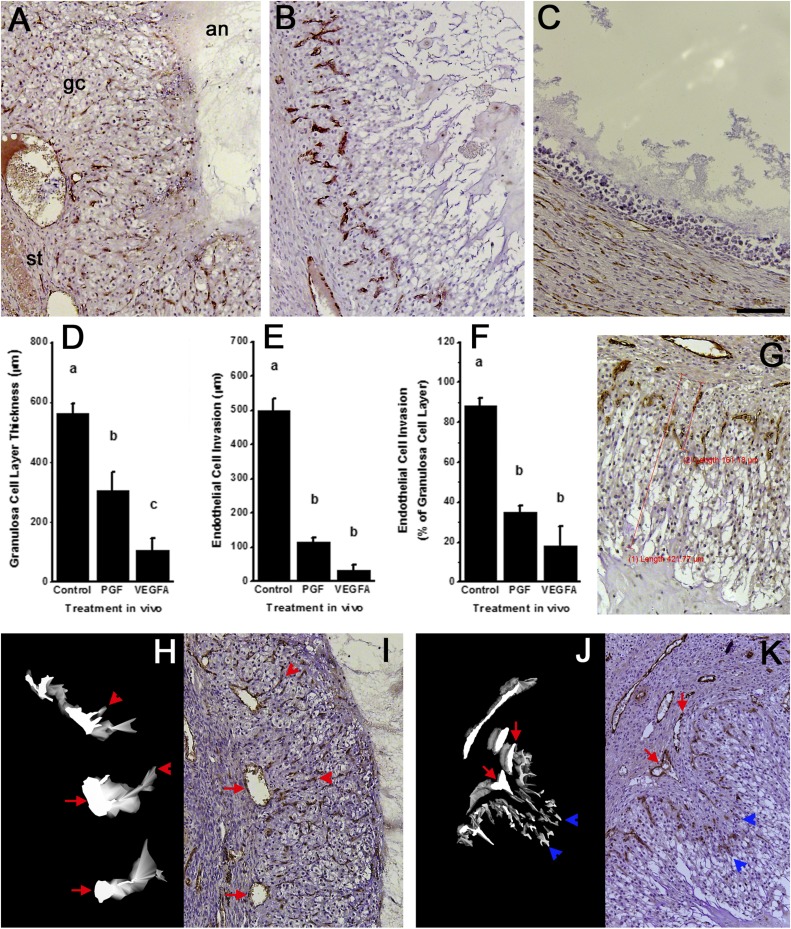
Figure 5.
Structural luteinization and angiogenesis in follicles after intrafollicular injection of antibodies against PGF or VEGFA. Top panels show histology of follicle wall after injection with (A) control IgG antibody, (B) PGF antibody, or (C) VEGFA antibody. All images are in same orientation, with stroma (st) lower left, granulosa cells (gc) central, and antrum (an) upper right as indicated in panel A. Endothelial cells are identified as vWF+ cells (brown); nuclei are stained blue. Graphs show morphometric analysis of (D) granulosa cell layer thickness and (E) endothelial cell invasion into the granulosa cell layer as distance from granulosa cell basement membrane to outermost edge of granulosa or endothelial cells, (G) as indicated by red lines on the accompanying image. (F) The ratio of endothelial cell invasion to granulosa cell layer thickness is also shown. For each graph, data are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean and were assessed by ANOVA and Duncan post hoc test, groups with no common superscripts are different, P < 0.05. n = 3 to 5 ovaries per group. All histological images are at the same magnification; scale bar in panel (C) = 100 µm. (H and J) 3D modeling of endothelial cells (white on black background) is shown alongside (I and K) representative histological images of vWF immunostained ovarian tissues after injection with (H and I) control IgG antibody or (J and K) PGF antibody used for 3D modeling of endothelial cells. Red arrows indicate stromal vessels, red arrowheads indicate capillary-like structures that connect to a stromal vessel, and blue arrowheads indicate endothelial cells within the granulosa cell layer that lack connection to a stromal vessel. Images from control IgG antibody show four small vessels within the granulosa cell layer; all four small vessels connect to stromal vessel indicated with the red arrow in adjacent tissue sections not used for 3D model construction.