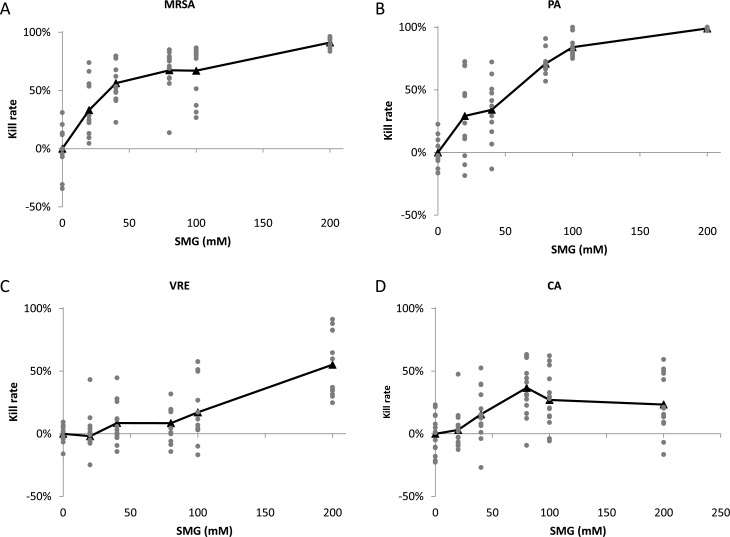
Figure 3.
Concentration-dependent bactericidal activity against (A) MRSA, (B) PA, (C) VRE, and (D) CA. In all of these experiments, BSA (10 mg/mL) and neutralizing buffer were added to the incubation mixtures to simulate a proteinaceous environment and to stop the reaction precisely, respectively. Pathogens were treated with 0 (control), 20, 40, 80, 100, and 200 mM SMG for 30 minutes, and kill rates were determined for each plate and plotted with gray dots. The average % kill rate was determined by the difference in the number of colony counts in treated versus control (untreated) samples and is expressed in black triangles. Each value represents the average of multiple (3–6) independent determinations carried out on a minimum of 3 separate days. SMG displayed greatest effects against MRSA and PA with marginal effects against VRE and was ineffective against CA. P value was calculated using regression models comparing differences in mean kill rates between doses adjusted for day (2-way ANOVA).