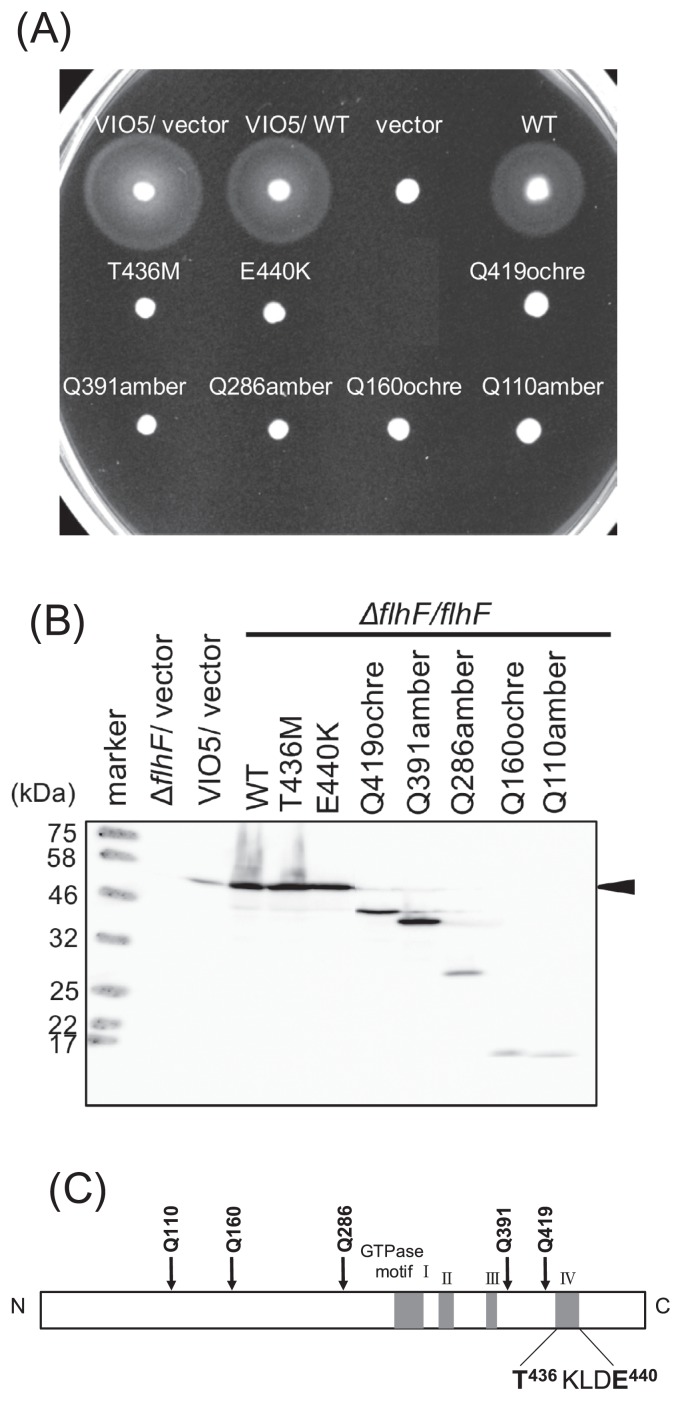
Figure 1.
Characterization of flhF mutations. (A) Cells of strain VIO5 (wild type) or LPN1 (ΔflhF mutant) harboring a plasmid— “vector” (pBAD33), +”WT” (pAK322), or a mutant plasmid (T436M, E440K, Q419ochre, Q391amber, Q286amber, Q160ochre, Q110amber) —were inoculated into a soft agar plate containing 0.02% arabinose and incubated for 4 hours at 30°C. (B) Detection of the FlhF protein. Proteins were induced by 0.02% arabinose in the cells as in panel (A) and immunoblotting was performed using an anti-FlhF antibody. (C) A schematic diagram of FlhF. The mutations obtained in this study are indicated. T436 and E440 are located in the putative GTPase motif of FlhF.