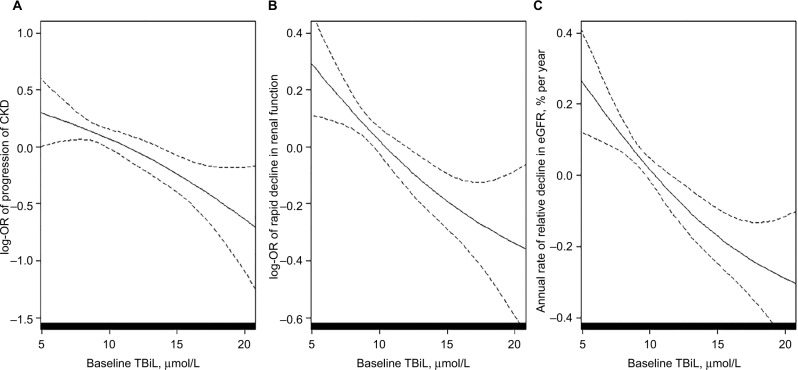
Figure 2.
The association between total bilirubin concentrations and progression of CKD (A), rapid decline in renal function (B), and annual rate of eGFR decline (C) in a post hoc analysis of the renal sub-study of the China Stroke Primary Prevention Triala (CSPPT).
Notes: aAdjusted for age, sex, treatment group, smoking status, alcohol intake, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, eGFR, proteinuria, serum glucose, total cholesterol, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate transaminase at baseline, as well as time-averaged systolic blood pressure during treatment.
Abbreviations: CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; TBiL, total bilirubin; OR, odds ratio.