Figure 2.
A Point Mutation in MAC7 Is Responsible for the Morphological and Molecular Phenotypes in the mac7-1 Mutant.
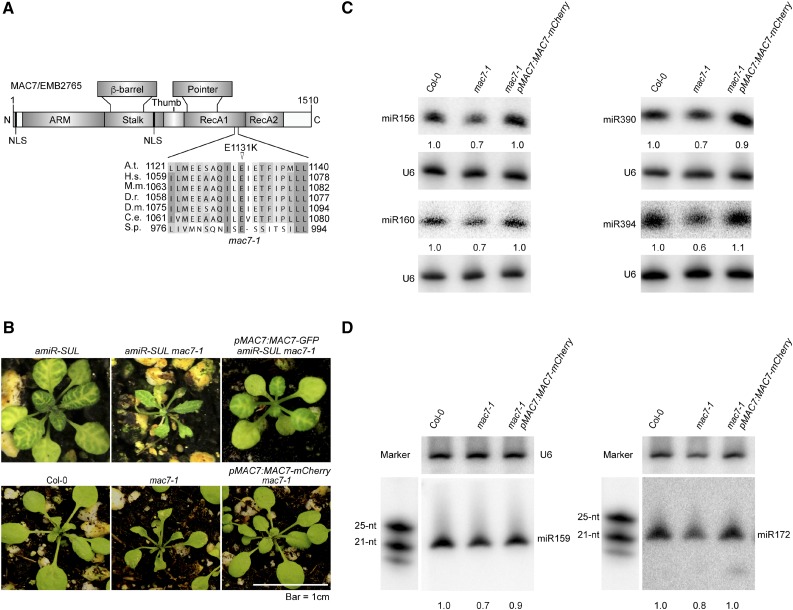
(A) A diagram of the MAC7 protein showing various domains, the predicted nuclear localization signal (NLS), and the E1131K mutation in the mac7-1 mutant. A sequence alignment of MAC7 and its orthologs in the region containing the E1131K mutation in the mac7-1 mutant is also shown. Abbreviations for species are as follows: Arabidopsis thaliana (A.t.), Homo sapiens (H.s.), Mus musculus (M.m.), Danio rerio (D.r.), Drosophila melanogaster (D.m.), Caenorhabditis elegans (C.e.), and Schizosaccharomyces pombe (S.p.). N, N terminus; ARM, armadillo domain; RecA, RecA-like domains; C, C terminus. The point mutation site is labeled by a triangle.
(B) Morphological phenotypes of 3- to 4-week-old seedlings of the indicated genotypes. pMAC7:MAC7-GFP and pMAC7:MAC7-mCherry were transformed into amiR-SUL mac7-1 and mac7-1, respectively.
(C) and (D) RNA gel blotting analysis of miRNAs from Col-0, mac7-1, and the complementation line mac7-1 pMAC7:MAC7-mCherry using inflorescences (C) and 12-d-old seedlings (D). The miRNA signals were quantified as described in Figure 1D. RNA markers (NEB, N2102S) shown in (D) were resolved in the same gel as miRNAs and probed separately by a DNA probe complementary to the marker sequences.