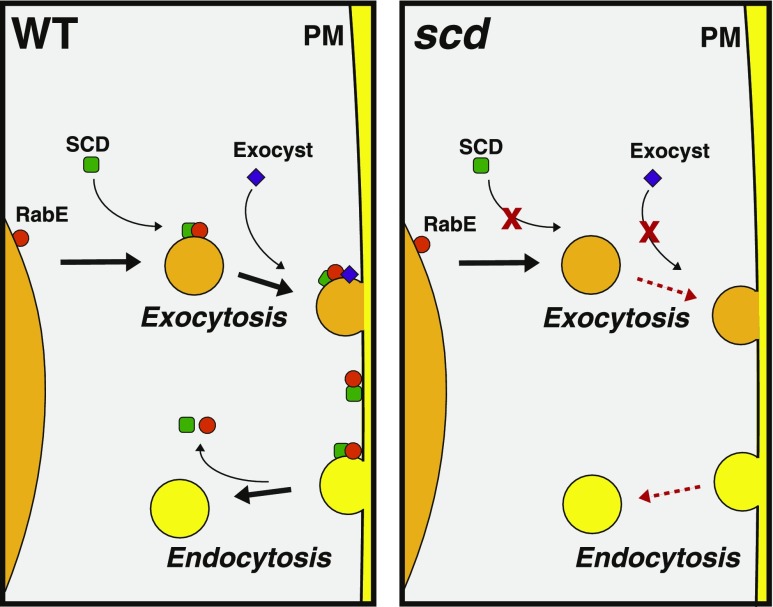
Figure 7.
SCD Function in Post-Golgi Trafficking.
In wild-type cells (left panel), the SCD complex (green square) associates with RabE1 (orange circle) and the exocyst complex (purple diamond) on exocytic post-Golgi vesicles. Following vesicle fusion, the SCD complex and RabE1 are deposited at the plasma membrane. In addition to its role in exocytosis, the SCD complex may function directly or indirectly in endocytosis as scd mutants exhibit exocytic as well as endocytic trafficking defects (Figure 2; McMichael et al., 2013). Our working model is that SCD-dependent exocytosis may deliver factors to the plasma membrane required for endocytosis and/or that following delivery to the cell surface, the SCD complex and activated RabE1 serve a role in the initiation of endocytosis. In scd mutants (right panel), activation and/or recruitment of RabE1 and the exocyst to post-Golgi secretory vesicles is impaired, leading to defects in exocytosis and endocytosis. Black arrows denote the direction of normal membrane trafficking. Red dashed arrows represent inhibition in membrane trafficking. PM, plasma membrane.