Figure 4. Nanotechnology-based approaches to modify the immune response to enhance humoral or cellular responses.
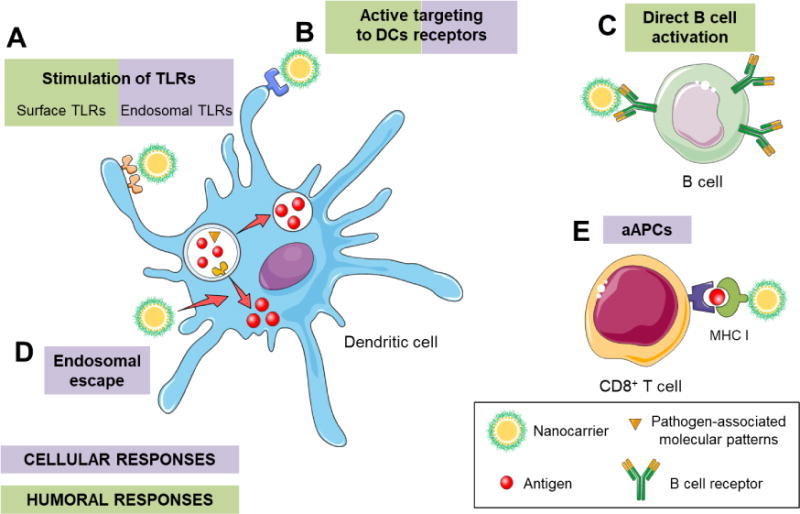
Nanocarriers can drive both humoral and cellular responses, depending on their features and composition. (A) Nanocarriers can deliver toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists that can activate surface or endosomal receptors, driving humoral or cellular responses, respectively. (B) Decorating nanocarriers with antibodies against specific receptors of dendritic cells (DCs) (e.g., CD40, CD11c, DEC-205, mannose, etc.) can activate these cells. (C) The direct targeting to B cells can stimulate them and, thus, favor antibody production and humoral responses. (D) Nanocarriers with properties that promote endosomal escape of the antigens, favor cellular responses. (E) A direct activation of CD8+ T cells through artificial antigen presenting cells (aAPCs) stimulates cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
