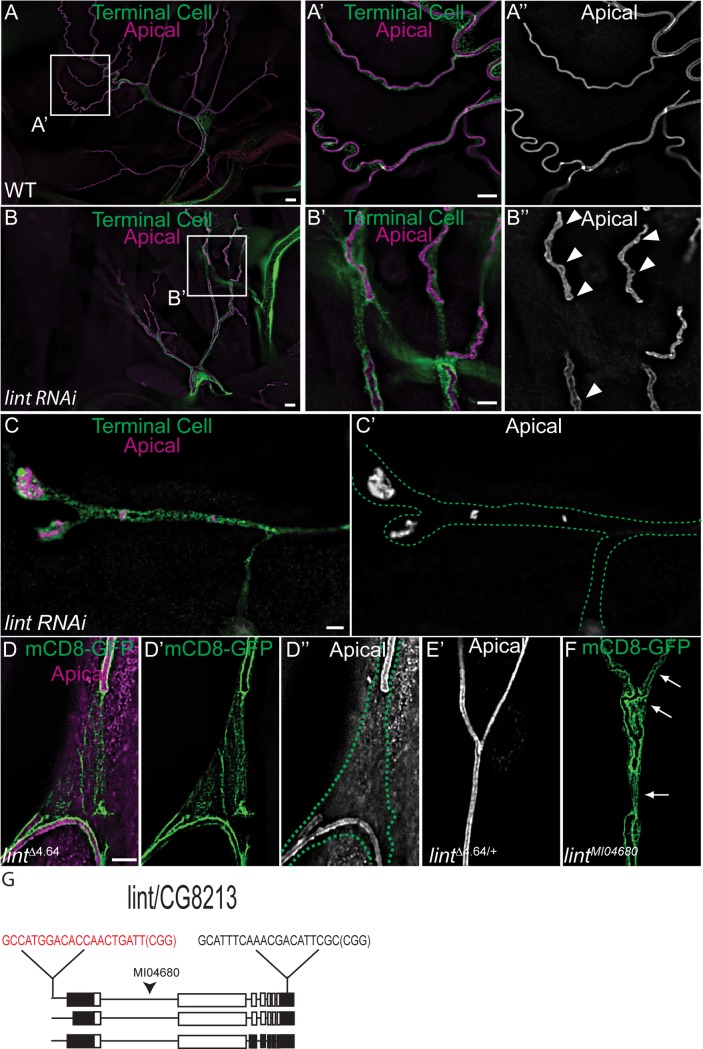
Fig 8. lumens interrupted (lint) is required for seamless tube integrity in terminal cells.
Wild type (WT, SRF>eGFP) control (A-A”) and short hairpin RNA against CG8213 expressing terminal cells (B-B”) were examined for apical membrane integrity. In contrast to control terminal branch seamless tubes (A’, A”), seamless tubes in lint-depleted terminal cells exhibit cystic dilations (arrowheads in B”), and discontinuities of the apical membrane with 100% penetrance (n = 33 terminal cells) (B’.B”). The most severely affected SRF>eGFP,CG8213 RNAi terminal cells are severely pruned with terminal branches largely devoid of luminal membrane, except for isolated inclusions. Terminal cell outlines are shown by green dots (C,C’). (D-D”) Details of lintΔ4.64 seamless tube defect from a mCD8-GFP-expressing terminal cell clone. The outline of the terminal cell is indicated by green dots. The seamless tubes of a neighboring heterozygous terminal cell (mCD8-GFP negative) are shown in (E’). The gRNA sequences used to target lumens interrupted (lint) using CRISPR/Cas9 are indicated in (G) on a schematic depicting lint gene organization with CDS in white and UTR sequences in black. The gRNA site indicated in red appears to be the site targeted by Cas9. (F) Detail of a lintMI04680 terminal cell clone expressing membrane-anchored GFP, which accumulates preferentially at the apical membrane. The arrows indicate discontinuities in the apical membrane. The position of the lethal transgene insertion is indicated in (G). (Scale Bars: A, B 20 μm; A”, B”, C and C’, D-F 5 μm).