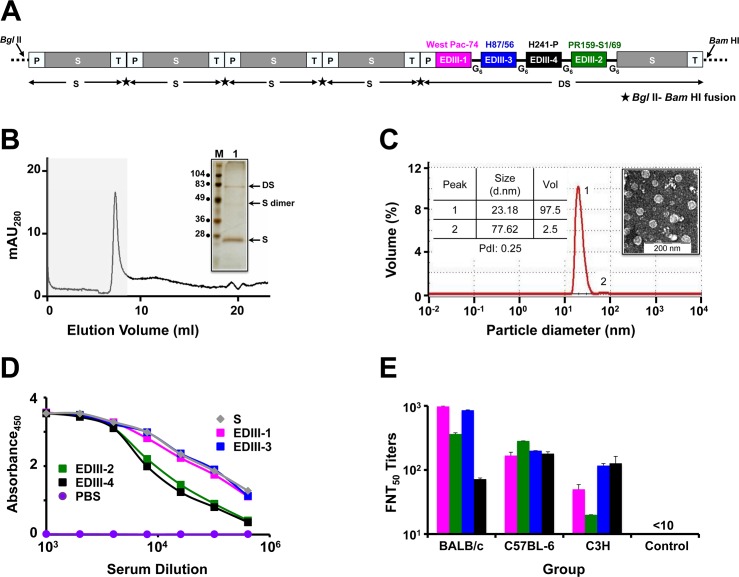
Fig 1. DSV4 assembles into immunogenic VLPs.
(A) Schematic representation of DSV4 antigen construct. Magenta, green, blue, and black blocks represent EDIII-encoding domains of DENV-1, -2, -3 and -4, respectively (the specific strains are indicated on the top of respective blocks). EDIIIs were linked to each other and to fusion partner Hepatitis B surface antigen (S; adw serotype; grey colored block), in frame, through hexa-glycyl (G6) linkers to encode Dengue-HBsAg (DS) protein. Four expression cassettes of S and one expression cassette of DS were assembled in pAO815 vector between Bgl II and Bam HI sites. Each expression cassette consists of 5’ AOX1 promoter (P), the recombinant gene (S or DS) and transcription terminator sequences (T). All the expression cassettes are in tandem, with the black star between adjacent expression cassettes representing Bgl II-Bam HI fusion site. (B) Elution of purified DSV4 in void volume (grey shaded region) of a Superose 6 column. The inset shows a silver stained gel picture of the material eluted in the void volume (lane ‘1’) with positions of DS, S and dimer of S indicated by arrows on the right. Protein size markers were run in lane ‘M’; their sizes (in kDa) are shown on the left. (C) Volume distribution profile of DSV4 using DLS. The left inset shows DLS parameter values (size, volume and PdI) for peaks 1 and 2. The right inset shows transmission electron microscopic image of DSV4 VLPs. (D) Indirect ELISA reactivity of pooled serum (n = 6) collected 15 days after completion of immunization of BALB/c mice (immunized on days 0, 30 and 90) with DSV4 adsorbed on alhydrogel. Serum was analyzed using purified recombinant EDIII-1 (magenta curve), EDIII-2 (green curve), EDIII-3 (blue curve), EDIII-4 (black curve) and HBsAg (grey curve) as capture antigen. PBS-immunized sera (purple curve) served as negative control. Each data point represents the average of duplicates. (E) Groups (n = 6) of three different mouse strains (BALB/c, C57BL-6 and C3H) were immunized with DSV4 VLPs as described in methods. A fourth group (n = 6, BALB/c) was immunized with S VLPs to serve as negative control. DSV4 and S VLPs were formulated in a mixture of alhydrogel plus MPLA for this experiment alone. Immune sera from all groups were analyzed for nAb titers (FNT50 titers) using the FACS assay against WHO reference strains of DENV-1 (magenta bars), DENV-2 (green bars), DENV-3 (blue bars) and DENV-4 (black bars). Mann-Whitney test-derived p values for DENV-1 (0.130), DENV-2 (0.959), DENV-3 (0.160) and DENV-4 (0.573) indicated no statistically significant difference in nAb titers between BALB/c and C57BL-6 mice. C3H mice elicited significantly lower nAb titers against DENV-1 (p = 0.007) and DENV-2 (p = 0.004), compared to BALB/c mice, and against DENV-2 (p = 0.006), compared to C57BL-6 mice.