Figure 2. Tobacco carcinogen-mediated LUAD pathogenesis in the Gprc5a-/- mouse.
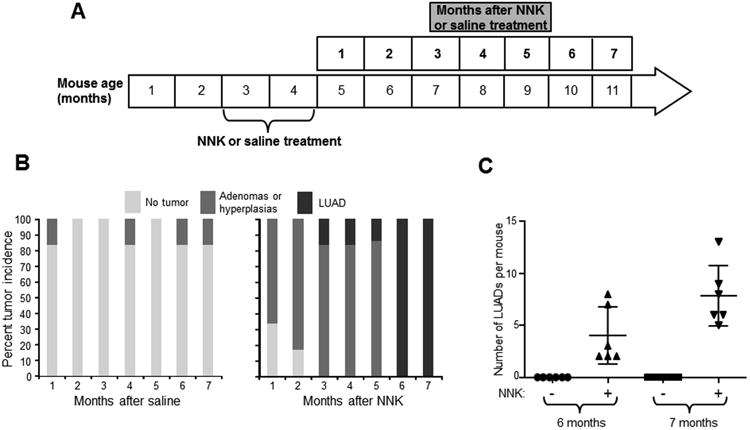
A. Schematic depicting timeline of NNK (three times 50mg/kg body weight per week for eight weeks) or saline treatment of eight weeks old Gprc5a-/- mice (see Methods). Mice were divided into groups of five to six mice (per treatment and time point) and were sacrificed at every month for seven months following saline and NNK treatment. B. At each of the indicated time points, mice lungs were histopathologically evaluated for the development of lesions. The lesions were pathologically categorized (hyperplasias, adenomas and adenocarcinomas) based on previously reported guidelines for murine lung lesions (23) and were then enumerated and compared and contrasted across time points and between treatment groups. C. LUAD burdens, indicated by the number of LUADs per mouse, were statistically compared and contrasted at six and seven months following NNK treatment.
