Figure 4. Whole-exome sequencing analysis of spontaneous and NNK-derived Gprc5a-/- LUADs.
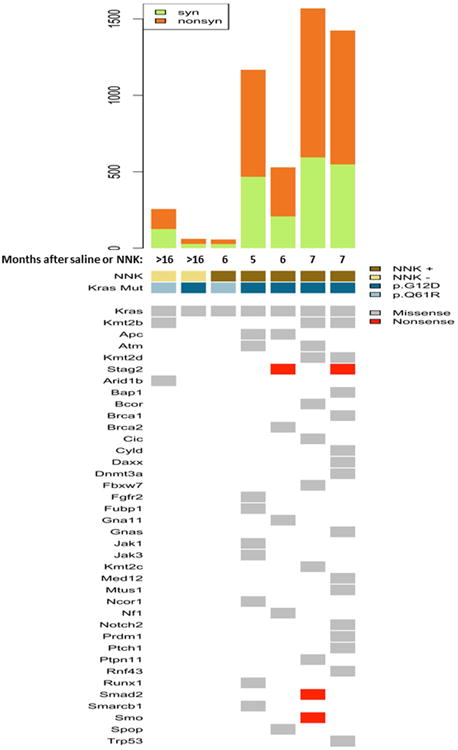
Two spontaneous (> 16 months following saline) LUADs from two Gprc5a-/- mice as well as five LUADs that developed in different mice by five to seven months following NNK treatment were analyzed by whole-exome sequencing (WES) as described in Materials and Methods. Somatic calls were contrasted against whole-exomes from three tail veins (from two Gprc5a-/- and one WT mice) and Gprc5a-/- normal lung tissues at one month following saline (see Methods). Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) were prioritized based on variants occurring in bona fide driver genes 27. The top panel depicts total number of silent (syn) and non-silent (nonsyn) exonic mutations per LUAD. In the lower panel, columns represent LUADs and rows represent mutated driver genes. Arrow indicates somatic Kras (p.G12D or p.Q61R) mutations.
