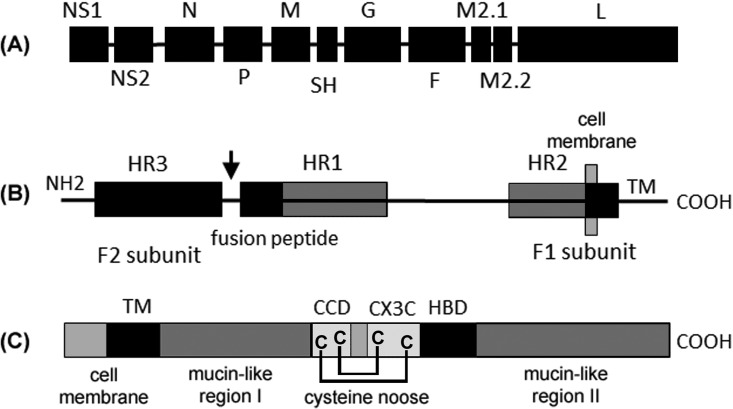
FIG 1.
RSV genome. (A) Ten genes produce 11 proteins. The M2-2 open reading frame (ORF) is accessed by ribosomes that reinitiate after exiting the M2-1 ORF. The G protein is produced as both membrane-bound and secreted forms via alternative translation start sites. Two antigenic subgroups (A and B) are defined by the hypervariable mucin-like regions of the G protein. (B) RSV F protein (575 amino acids [aa]) is cleaved by furin (at the arrow) to produce the F1 and F2 domains with a conformational change that promotes fusion with cell membranes; the location of heptad repeats (HR), fusion peptide, and transmembrane domain (TM) are shown. (C) The RSV G protein (298 aa) central conserved domain (CCD) includes a conformationally constrained CX3C motif (182-CWAIC-186) that is implicated in infection of lung epithelial cells through binding to CX3CR1, assisted by a heparin binding domain (HBD). The MAb TRL3D3 binds to an epitope within the CCD.