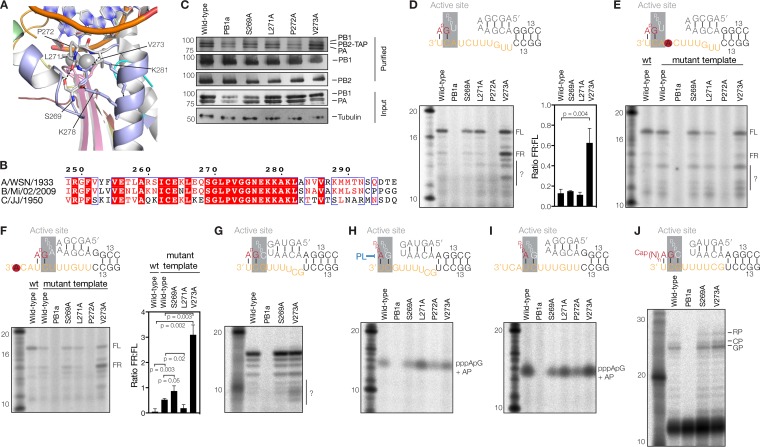
FIG 2.
PB1 V273 affects priming and realignment. (A) Superposed structure of the bat influenza A virus RdRp (PDB accession number 4WSB) with the poliovirus 3Dpol RdRp elongation complex (PDB accession number 3OL7). For the 3Dpol complex, the template strand, nascent strand, and magnesium ions are shown. For the bat influenza A virus RdRp, the PB1 subunit is shown in light blue, with polymerase motifs A, C, D, and F shown in yellow, pink, red, and pale green, respectively. Polar interactions between amino acids of the helix-loop-helix structure are indicated with dotted lines. Additional side chains are shown for reference. (B) Amino acid alignment of the PB1 helix-turn-helix structure of the palm subdomain. PB1 sequences of influenza A/WSN/33 (H1N1), influenza B/Michigan/22687/09, and influenza C/JJ/50 viruses are shown. Identical residues are shaded red, and conserved residues are surrounded with blue boxes. Secondary-structure annotations are based on data reported under PDB accession number 4WSB. (C) SDS-PAGE and silver staining of recombinant influenza A virus RdRps isolated from HEK 293T cells or Western blot analysis of PB1 and PB2 in isolated RdRps. The bottom panel shows the expression of PB1 and PA RdRp subunits in HEK 293T cells. A tubulin loading control is also shown. (D) ApG extension on a cRNA promoter. The graph shows the ratios of the quantified FR and FL signals of three independently purified RdRp sets. The P value was determined by using an unpaired t test. Unknown products are indicated with a question mark. (E) ApG extension on the 4U→A mutant cRNA promoter. The question mark indicates an increase in the amount of unknown RNA products. (F) ApG extension on the 1U→A mutant cRNA promoter. The graph shows the mean FR-to-FL product ratios for three independently purified RdRp sets. The P values were determined by using an unpaired t test. (G) ApG extension on a vRNA promoter. Unknown products are indicated with a question mark. In each graph, the error bars indicate standard deviations (n = 3). (H) Terminal pppApG synthesis on a cRNA promoter in the presence of ATP and [α-32P]GTP. The reaction mixtures were treated with alkaline phosphatase (AP) to better separate the radioactive product from the nonincorporated [α-32P]GTP and free phosphates. (I) Internal pppApG synthesis on a vRNA promoter. (J) Extension of a radiolabeled capped 11-nucleotide-long RNA primer ending in 3′ AG. This extension reaction yields a product initiated at G3 (GP) or a product initiated at 2C (CP) of the vRNA promoter and an additional realignment product (RP) (40).