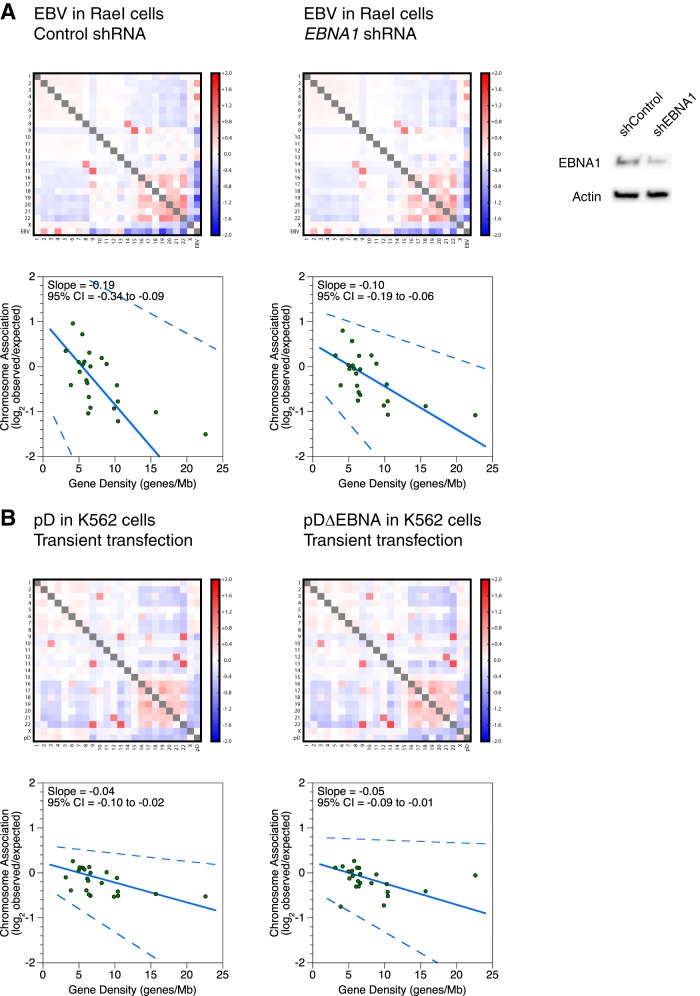
FIG 4.
Tests of if EBNA1 is necessary to reconstitute chromosome association preferences of full-length EBV. (A and B) Interchromosomal contacts involving the pD plasmid, the pDΔEBNA plasmid, EBV genomes, and human genomes in the RaeI and K562 cell lines as measured by Hi-C. Heat maps of chromosome associations between chromosomes and between each human chromosome and the EBV genome, pD plasmid, or pDΔEBNA plasmid are shown. Observed counts are normalized against random expectation and shown on a log2 scale. Red indicates enrichment, and blue indicates depletion. Scatterplots depict virus-human chromosome associations plotted against the gene density of each chromosome. A solid line indicates the Thiel-Sen fit, and dashed lines indicate the 95% confidence interval. In the heat maps, a gray box off the diagonal represents a score with an absolute value of >2. (A) Lentivirus-mediated shRNA depletion of the EBV EBNA1 protein in the RaeI cell line. Western blots depict EBNA1 and β-actin expression levels in whole-cell lysates after control or EBNA1 knockdown. (B) Deletion of the EBV EBNA1 gene in the pDΔEBNA plasmid in the K562 cell line. pD and pDΔEBNA were transiently transfected prior to measurement of interchromosomal contacts by Hi-C.