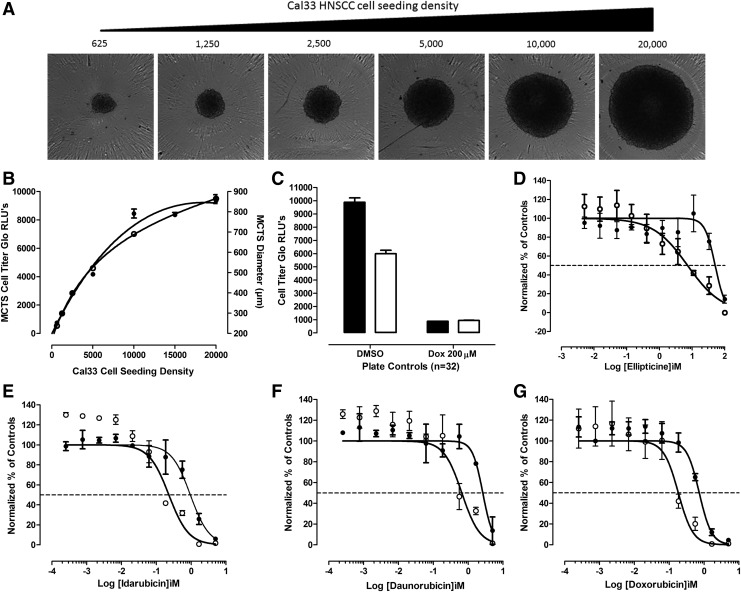
Fig. 1.
HNC MCTSs and comparison of cancer drug growth inhibition in 2D monolayer and 3D MCTS HNC culture models. (A) Transmitted light images of Cal33 MCTSs formed in 384-well ultra-low attachment plates seeded with different cell densities after 24 h in culture. Cal33 HNC cells were seeded into 384-well ULA plates at densities ranging from 625 to 20,000 cells per well and after 24 h in culture transmitted light images of the MCTSs were acquired on the IXM automated imaging platform by using a 4 × objective. Representative images from one of several independent experiments are shown. (B) Impact of Cal33 cell seeding density on MCTS CTG signals and diameters. The mean ± SD (n = 12) CTG RLUs (●) produced by MCTS formed in 384-well ULA plates at the indicated Cal33 cell seeding densities are plotted on the left Y-axis, and the mean ± SD (n = 2) diameters (μm) (○) of the MCTSs extracted from the transmitted light images by the single line tool of the MetaXpress image analysis software are plotted on the right Y-axis. Representative experimental data from one of several independent experiments are shown. (C) Cal33 2D monolayer and MCTS growth inhibition assay plate controls. To define the dynamic ranges of 72 h MCTS (□) and 2D monolayer (■) HNC growth inhibition assays, we used 0.5% DMSO control wells to represent uninhibited growth (Max., n = 32), and 200 μM doxorubicin +0.5% DMSO control wells to represent 100% of tumor cell cytotoxicity (Min., n = 32), respectively. The mean ± SD (n = 32) CTG RLUs from one of three to four independent experiments are shown. GI50 curves for Cal33 2D monolayer and MCTS cultures exposed to ellipticine (D), idarubicin (E), daunorubicin (F), or doxorubicin (G) for 72 h. Cal33 cells were seeded into 384-well monolayer assay plates at 1,000 cells per well (○), and into 384-well ULA plates at 5,000 cells per well (●). After 24 h in culture, the indicated concentrations of compounds were transferred into the test wells of assay plates that were then cultured for an additional 72 h before CTG detection reagent was added to the wells and the RLUs were captured on the SpectraMax M5e microtiter plate reader. The normalized mean ± SD (n = 3) growth inhibition data from triplicate wells for each compound concentration are presented. Representative experimental data from one of three to four independent experiments are shown. 3D, three-dimensional; CTG, CellTiter-Glo®; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; GI50, 50% growth inhibitory concentration; HNC, head and neck cancer; IXM, ImageXpress® Micro; Max., maximum plate controls; Min., minimum plate controls; MCTS, multicellular tumor spheroid; RLUs, relative light units; SD, standard deviation; ULA plates, ultra-low attachment microtiter plates.