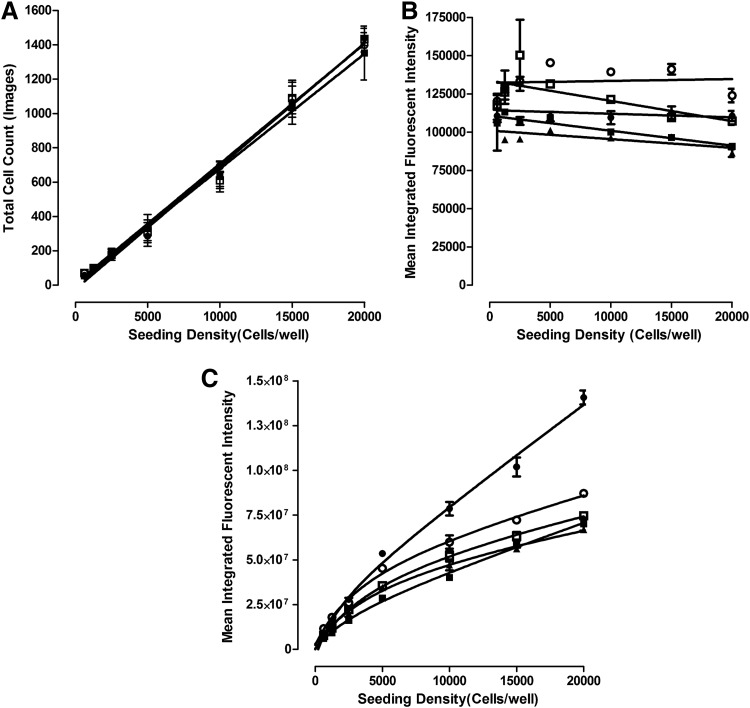
Fig. 6.
Effects of Cal33 HNC cell seeding density on fluorescent drug accumulation in 2D monolayers (A, B) and MCTSs (C). Cal33 cells were seeded into 384-well monolayer and MCTS assay plates at seeding densities of 625, 1,250, 2,500, 5,000, 10,000, and 20,000 cells per well. After 24 h in culture, test drugs were added at final concentrations of 10 μM and plates were then incubated for 15 min before fixation in formaldehyde containing Hoechst and washing with PBS. DAPI, FITC, and TRITC images of Cal33 monolayers and MCTSs were acquired on the IXM and analyzed by using the MWCS image analysis module as described earlier. (A) Cal33 monolayer cell counts versus seeding density. The mean ± SD (n = 3) total cell counts from triplicate wells for each monolayer cell seeding density are presented: ellipticine (●), idarubicin (○), doxorubicin (■), and daunorubicin (□). (B) Cal33 monolayer fluorescent drug accumulation versus cell seeding density. The mean ± SD (n = 3) of the mean integrated fluorescent intensities from triplicate wells for each monolayer cell seeding density are presented: ellipticine-FITC (●), idarubicin-FITC (○), idarubicin-TRITC (▲), doxorubicin-TRITC (■), and daunorubicin-TRITC (□). (C) Cal33 MCTS fluorescent drug accumulation versus cell seeding density. The mean ± SD (n = 3) of the mean integrated fluorescent intensities from triplicate wells for each MCTS cell seeding density are presented: ellipticine-FITC (●), idarubicin-FITC (○), idarubicin-TRITC (▲), doxorubicin-TRITC (■), and daunorubicin-TRITC (□). Representative data from one of three independent experiments are shown.