Figure 4.
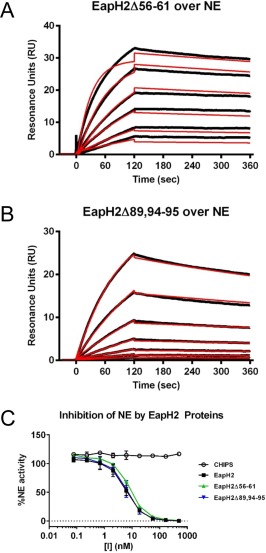
Residues Arg89, Glu94, and Lys95 are not required for EapH2 function. The contributions of EapH2 residues corresponding to positions required for EapH1 inhibition of NE were probed by a combination of site‐directed mutagenesis, NE‐binding measurements, and functional assays. Binding of EapH2 mutants EapH2Δ56–61 (A) and EapH2Δ89,94–95 (B) to an NE surface was assessed by SPR. The reference subtracted sensorgrams are shown in black, while the results of curve fitting to a Langmuir binding model are shown in red. (C) The impact of site‐directed mutations in EapH2 on NE activity was monitored by a fluorometric activity assay. All data points were measured in duplicate, and error bars depict SD. A legend is inset.
