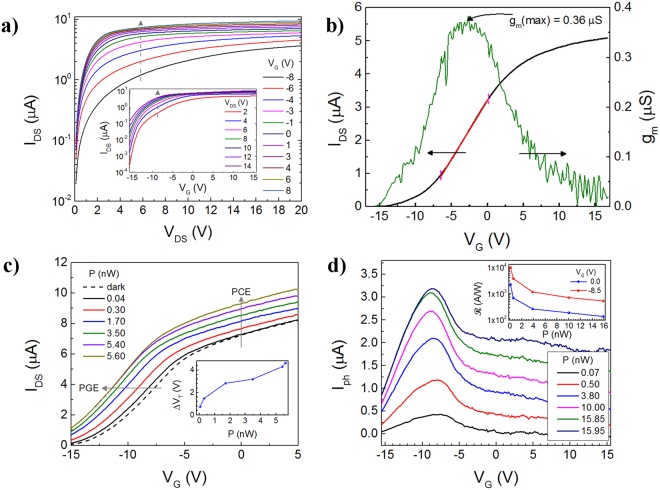
Figure 4.
Three-terminal optoelectronic measurements in the MSM suspended MoS2 PD. (a) IDS-VDS characteristic at varying VG in dark. Inset shows IDS-VG characteristics from which an ON/OFF ratio was calculated to be ~104 at VDS = 2 V. (b) IDS-VG transfer characteristics for varying levels of P at VDS = 2 V, from which a maximum μFE of ~42.7 cm2V−1s−1 was calculated at peak gm ~ 0.36 μS based on Equation 5. (c) Iph as a function of VG to analyze the photocurrent generation mechanism, where the highest was found at ~−8.5 V. The photogating effect (PGE) is also seen to be effective here since a shift in voltage of ~−1.1 V is seen and the shift to the left indicates p-type trap states. At the same time, the photoconductive effect (PCE) appears to be the dominant photocurrent generation mechanism since Iph shifts up in the y direction45. (d) Iph as a function of VG, the highest sensitivity is shown at VG = −8.5 V where the conductance is the minimum. The inset shows as a function of P at VG = 0 V and −8.5 V, respectively for VDS = 5 V. All the measurements where performed at 300 K and in vacuum.