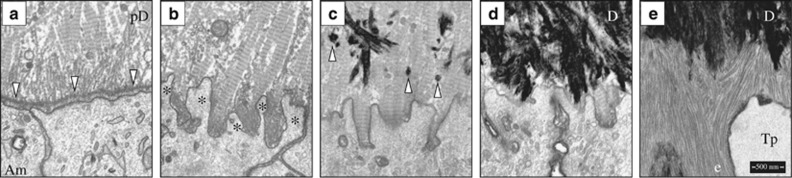
Figure 2.
Focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) images of early dentin and enamel mineralization in the mouse mandibular incisor. (a) The tips of unmineralized type I collagen predentin (pD) matrix deposited by odontoblasts (not shown) pass through the basement membrane (downward arrowheads) and associate with the ameloblast (Am) plasma membrane. (b) Fenestration of the basement membrane and the extension of ameloblast processes (*) into the unmineralized collagen matrix. (c) The onset of dentin mineralization as discrete mineral foci (upward arrowheads); (d) expansion of the dentin (d) mineral into a continuous layer; and (e) deposition of enamel mineral ribbons (e) on mineralized dentin. The ameloblast has already formed a Tomes process (Tp) that organizes the ribbons into rod and interrod enamel. FIB-SEM technology is allowing scientists to obtain ultrastructural information of enamel formation in wild-type and knockout mice.