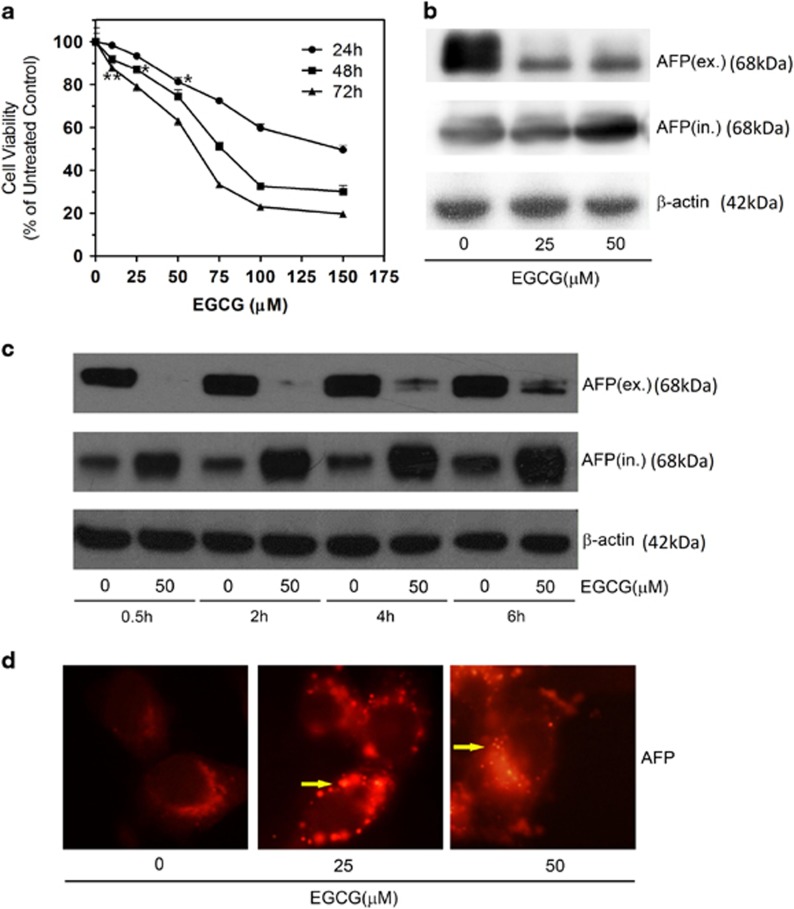
Figure 1.
EGCG induces AFP aggregation in HepG2 cells. (a) MTT assay of HepG2 cells after 0–150 μM EGCG treatment (with FBS) for 24, 48, and 72 h. *P<0.05 (t=2.72 for 24 h, t=2.83 for 48 h) and **P<0.01 (t=5.30 for 72 h), the treated groups were compared with an untreated control (considered to be 100% viable). The data are presented as mean±S.D. derived from three independent experiments. (b) Western blot assay of intracellular and extracellular AFP. HepG2 cells were treated in the absence or presence of 25 and 50 μM EGCG for 24 h. (c) HepG2 cells were incubated with or without 50 μM EGCG for 0–6 h, and intracellular and extracellular protein were subjected for western blotting analysis. (d) HepG2 cells were treated with 0, 25, and 50 μM EGCG for 24 h, respectively, and stained with AFP-specific primary antibody and CY3-conjugated secondary antibody. Yellow arrows: aggregated AFP protein (× 40)