Figure 1.
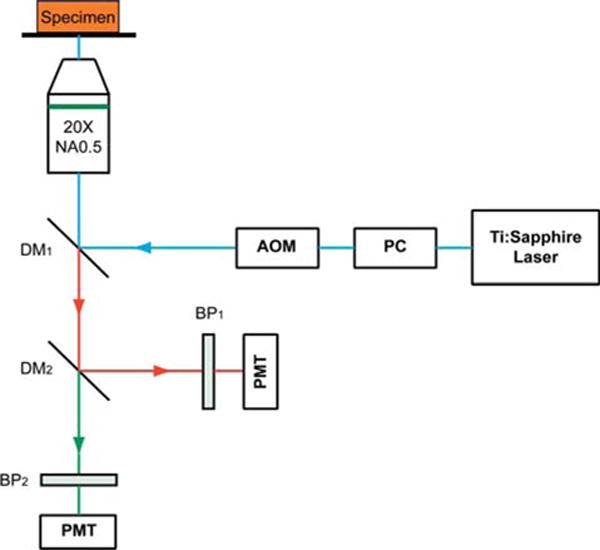
Schematic illustration of the optical set-up. Excitation laser was a tunable mode-locked Ti : Sapphire laser (710 nm to 990 nm set at 900 nm) with a pulse compressor (PC) for dispersion compensation and an acousto-optic modulator (AOM) for power control. The laser passed through a dichroic mirror, DM1, an objective lens (20×, NA = 0.5), before reaching the tissue specimen. Two-photon excited fluorescence (TPEF) was collected by the objective lens in the epi-mode, filtered by a 500–550 nm band-pass filter, BP1, before being recorded by a photomultiplier tube (PMT). Reflective second harmonic generation (SHG) signal was similarly collected as TPEF, through a 390–465 nm band-pass filter, BP2, with another PMT.
