Figure 2.
RPAP1 Is Required for the Establishment and Maintenance of Cell Identity
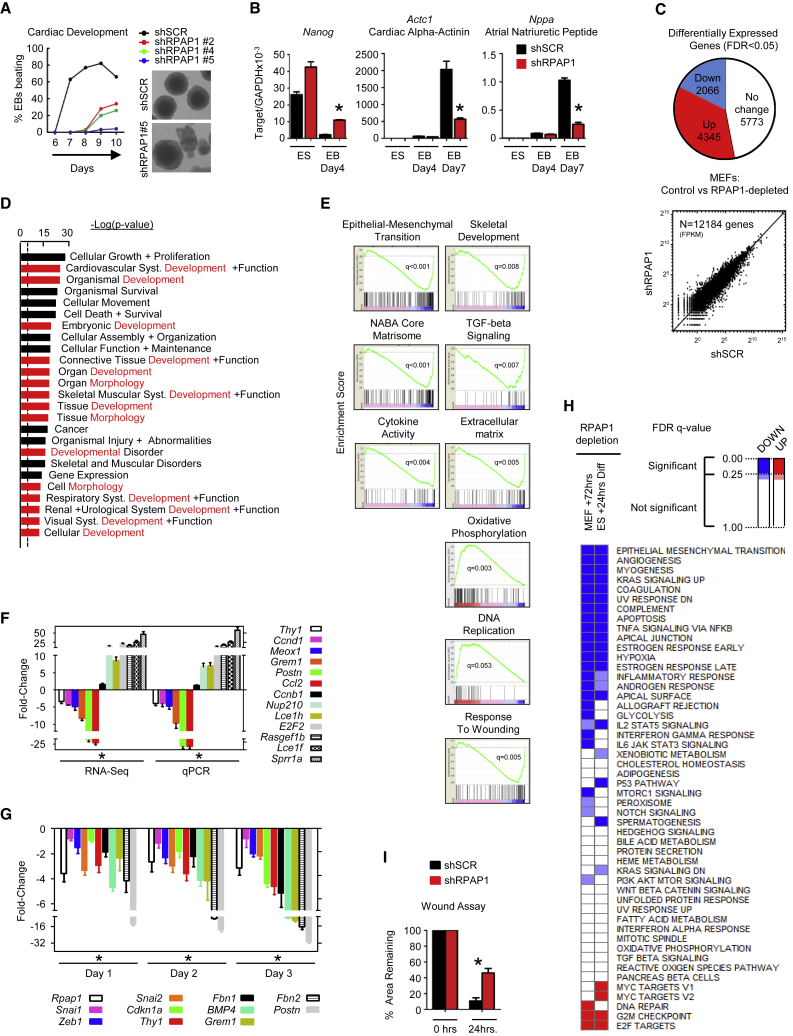
(A) Effect of RPAP1 depletion on embryoid body (EB) cardiac center development. EBs were scored daily by microscopy for the appearance of clusters of actively beating cells indicative of cardiac muscle development. The graph shows the kinetics over several days. Representative pictures of EBs are shown.
(B) qPCR analyses of pluripotency or cardiac development markers at the indicated time points from the EB differentiation assay in (A). Mean ± SD; n = 3 replicates; ∗p < 0.05.
(C) Overview of RNA-seq transcriptome analyses summarizing differential gene expression (FDR q < 0.05) in MEFs at day 3 after RPAP1 depletion. (Upper panel) Proportional representation pie chart of significantly differentially expressed genes is shown. (Lower panel) Dot plot of FPKM values for all genes shows that many genes of high and low expression level remain unchanged.
(D) Ingenuity pathway analysis showing the top 25 most significantly enriched GO terms among those genes that were significantly downregulated at day 3 after RPAP1 depletion in MEFs (FDR q < 0.01). Terms highlighted in red contain “development” or “morphogenesis.” Dotted line indicates the basal threshold of significance.
(E) Examples of the most significantly up- or downregulated gene sets identified by GSEA analysis in RNA-seq data at day 3 after RPAP1 depletion in MEFs (FDR q < 0.01). See also Figures S3J and S3K and Table S2.
(F) qPCR validation of RNA-seq data. Mesenchymal, fibroblast, and epithelial marker mRNA expression levels were assessed by RNA-seq (left) or qPCR (right) at day 3 after RPAP1 knockdown in MEFs. Data indicate fold change relative to control shSCR. Mean ± SD; n = 3 independent MEF lines; ∗p < 0.05.
(G) qPCR measurement of mesenchymal and fibroblast marker mRNA levels during days 1–3 lentiviral transduction of MEFs with non-targeting control (shSCR) or with RPAP1 targeting (shRPAP1) shRNAs. Data indicate fold change relative to control. Mean ± SD; n = 3 independent MEF lines; ∗p < 0.05. See also Figure S2L.
(H) Heatmap summarizing the most significantly up- or downregulated hallmark gene sets identified by GSEA analysis among all gene expression at day 3 after RPAP1 depletion in MEFs (FDR q < 0.01; left column; see Tables S2 and S3) or in ESCs 24 hr after triggering differentiation (FDR q < 0.05; right column; see Tables S1 and S2). Hallmark gene sets with FDR q < 0.25 are significant. Also highlighted in the heatmap are borderline gene sets (where FDR q = 0.35–0.25).
(I) Wound assay scratch test recovery. Graph shows the percent damaged area remaining at +24 hr. Mean ± SD; n = 3 independent MEF lines with 12 replicates each; ∗p < 0.05.