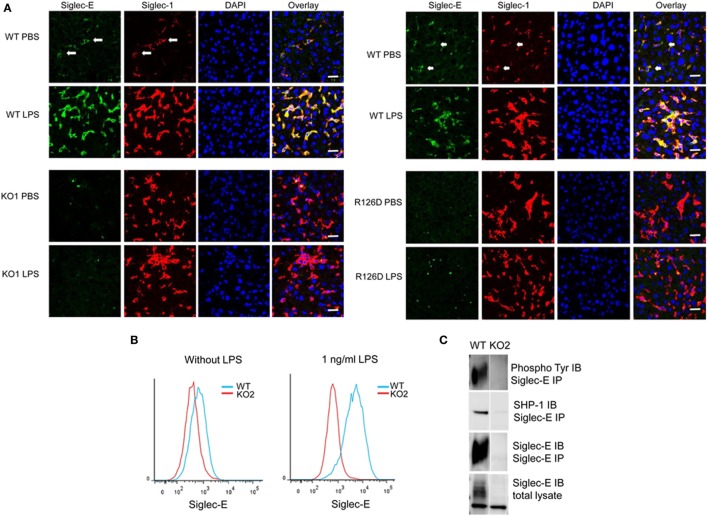
Figure 1.
Siglec-E expression on tissue macrophages and bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) is upregulated following lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment. (A) Wild-type (WT), KO1, and R126D mice were injected with 15 µg LPS or PBS intraperitoneally. After 3 h, animals were euthanized and tissue samples collected and frozen. Liver cryostat sections were labeled with sheep anti-siglec-E Ab directly labeled with Alexa 488 and anti-siglec-1 Abs SER-4 and 3D6 followed by anti-rat Alexa 647. Sections were also stained with DAPI to reveal nuclei. Siglec-E is expressed on Kupffer cells, which co-express siglec-1, and is upregulated following LPS stimulation in WT but not KO1 or R126D mice. Green dots in the anti-siglec-E stained KO1 and R126D sections are due to non-specific binding of the antibody (Ab). The scale bar represents 10 µm. (B) Siglec-E is expressed at low levels on BMDM and strongly upregulated following 3 days culture in 1 ng/ml LPS. (C) Siglec-E is constitutively phosphorylated in LPS-stimulated BMDM. WT and KO2 BMDM were treated for 3 days with 1 ng/ml LPS and the upregulated siglec-E was immunoprecipitated (IP) using sheep ant-siglec-E Ab and immunoblotted (IB) for phosphotyrosine, SHP-1 and siglec-E.