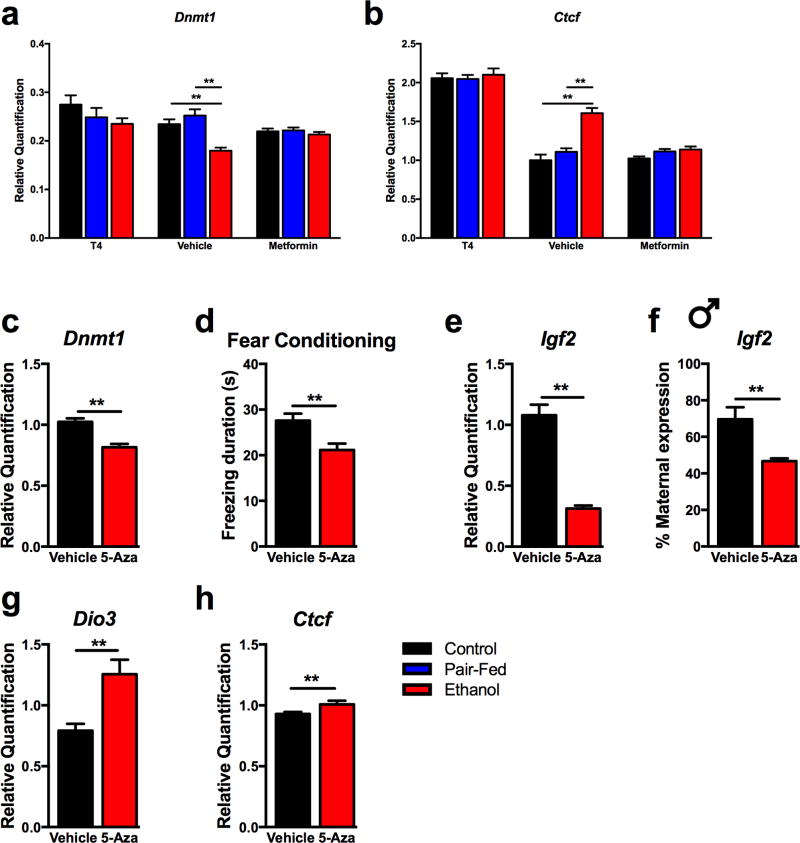
Figure 5. The role of Dnmt1 in FAE-induced deficits.
a) Hippocampal Dnmt1 expression was affected by FAE and alleviated by neonatal treatments (N = 7–20/prenatal diet/neonatal treatment, sex combined). b) Treatment-specific changes in adult hippocampal Ctcf expression (sex combined T4: N = 9–10/prenatal diet/neonatal treatment; Metformin: N = 7–13/prenatal diet/neonatal treatment). Data is normalized to Vehicle Control animals. c-h) Administration of Dnmt1 inhibitor 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine (5-Aza, 1 µg/gr/day, from postnatal day 1 to 10) to control neonates mimicked the effects of FAE in fear memory deficit and hippocampal gene expression changes in the adult offspring. N=13–14/neonatal treatment, sex combined, except f) N=4–5 males/neonatal treatment. Details are as described in Figure 1.