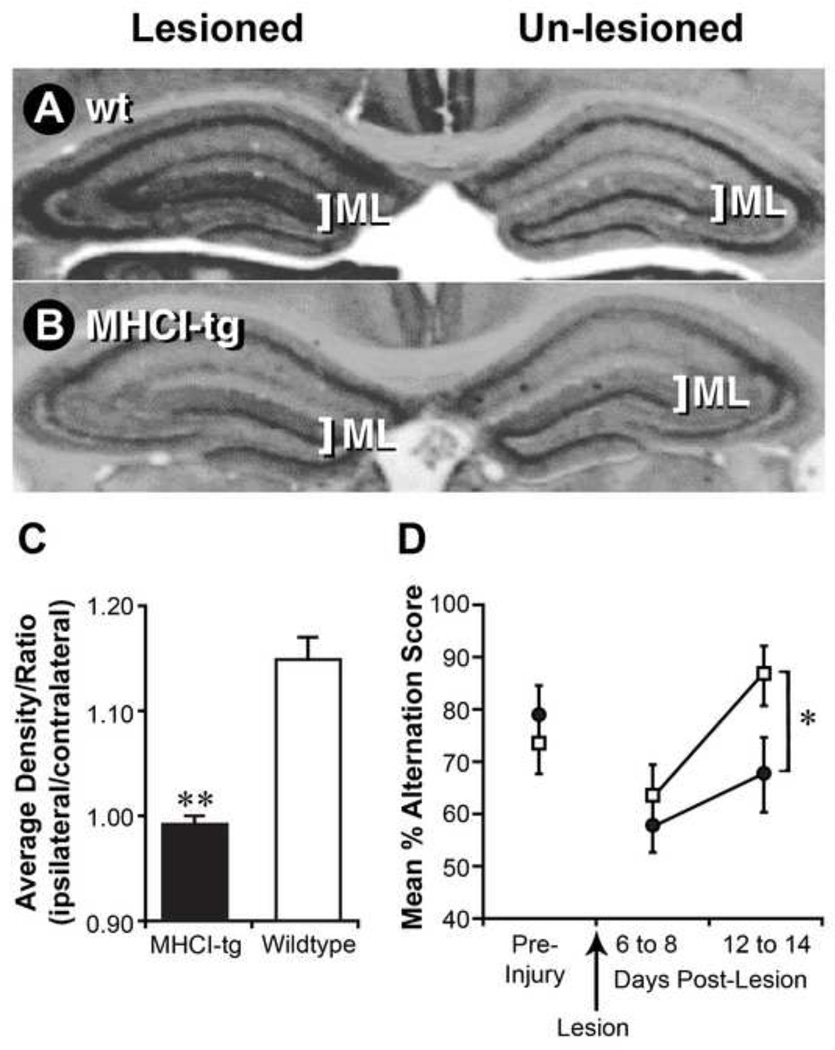
Fig. 5. NSE-Db mice have deficiencies in compensatory sprouting responses after hippocampal lesioning.
The perforant path of wildtype (wt) C57BL/6 or NSE-Db mice was unilaterally lesioned. After 14 days, coronal brain sections were stained for AChE. Representative AChE stained sections from lesioned wt (A) and NSE-Db mice (B). The AChE staining patterns on unlesioned side of wt and NSE-Db mice were similar. On the lesioned side, compensatory cholinergic sprouting responses occurred in the molecular layer (ML) of wt, but not NSE-Db mice. (C) Group data of the mean ratio (lesioned/unlesioned) AChE staining density in the ML of wt and NSE-Db mice ± SEM. **=p<0.001. (N=6–8 mice/group). (D) Wt (□) and NSE-Db (●) mice showed similar ability to perform a hippocampal-dependent spatial task preoperatively and similar deficits immediately following lesioning. By 12–14 days post-lesion wt mice recovered their ability to perform the task, while NSE-Db mice displayed recovery deficits. Data shown is mean percent alternation ± SEM (*=p<0.05). (N=15 mice/group).