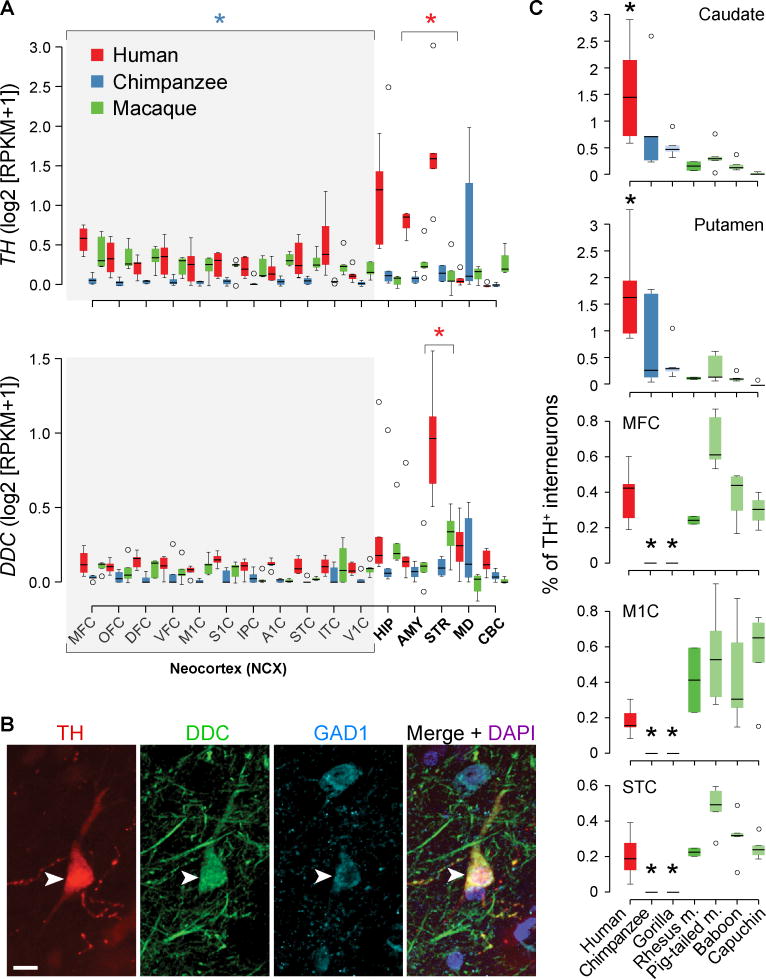
Fig. 4. Human-specific expression of genes encoding dopamine biosynthesis enzymes.
(A) TH and DDC, respectively, showing higher expression in the human striatum (STR). TH is also downregulated in the chimpanzee neocortex. Boxes represent quartiles and whiskers 1.5 times interquartile range. Red and blue asterisks represent human-specific differential expression in striatum and chimpanzee-specific differential expression combining all neocortical areas, respectively (FDR < 0.01). (B) Immunofluorescence shows co-localization of TH, DDC, and GAD1 in adult human neocortical interneurons (arrowheads). Scale bar represents 10 µm. (C) STR (caudate and putamen) shows an enrichment of TH+ interneurons in human. MFC, M1C, and STC show a complete depletion of TH+ interneurons in chimpanzee and gorilla. Asterisk represents Tukey's honest significance test P < 0.05 comparing human or chimpanzee/gorilla with all other species.