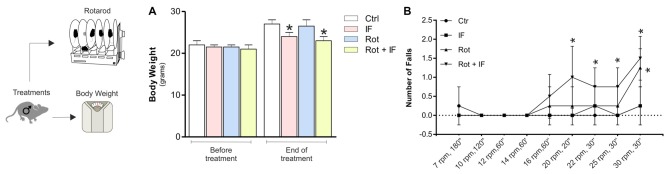
Figure 1.
Intermittent fasting (IF) causes motor dysfunction in rotenone-treated mice. (A) Body weight was recorded immediately before and at the end of treatment. Data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 4; F(7,8) = 5.60; *p < 0.05 vs. Ctr). (B) A rotarod test was performed at different times and speeds to evaluate motor function (n = 4, F(3,12) = 4.01; *p < 0.05 vs. Ctr).