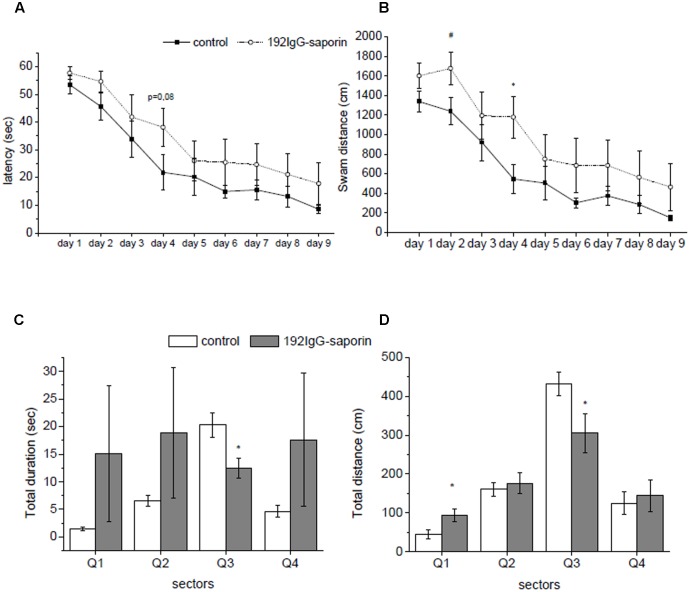
FIGURE 1.
The effects of intraventricular injection of 192IgG-saporin (Ig-saporin) on spatial memory in Morris water maze task. Ig-saporin injected rats (n = 8) had longer latencies to reach the platform (seconds) (A) and higher distance swam (centimeter) (B) compared to control (n = 8) during the 9 days when the animals learned to find platform. On day 10 of testing, during probe trial saporin-treated rats (n = 8) spent significantly less time in a quadrant, where the platform was during training (C), and swam shorter distance in it compared to the control (n = 8) (D). Each point represents the mean ± SEM, ∗P < 0.05.