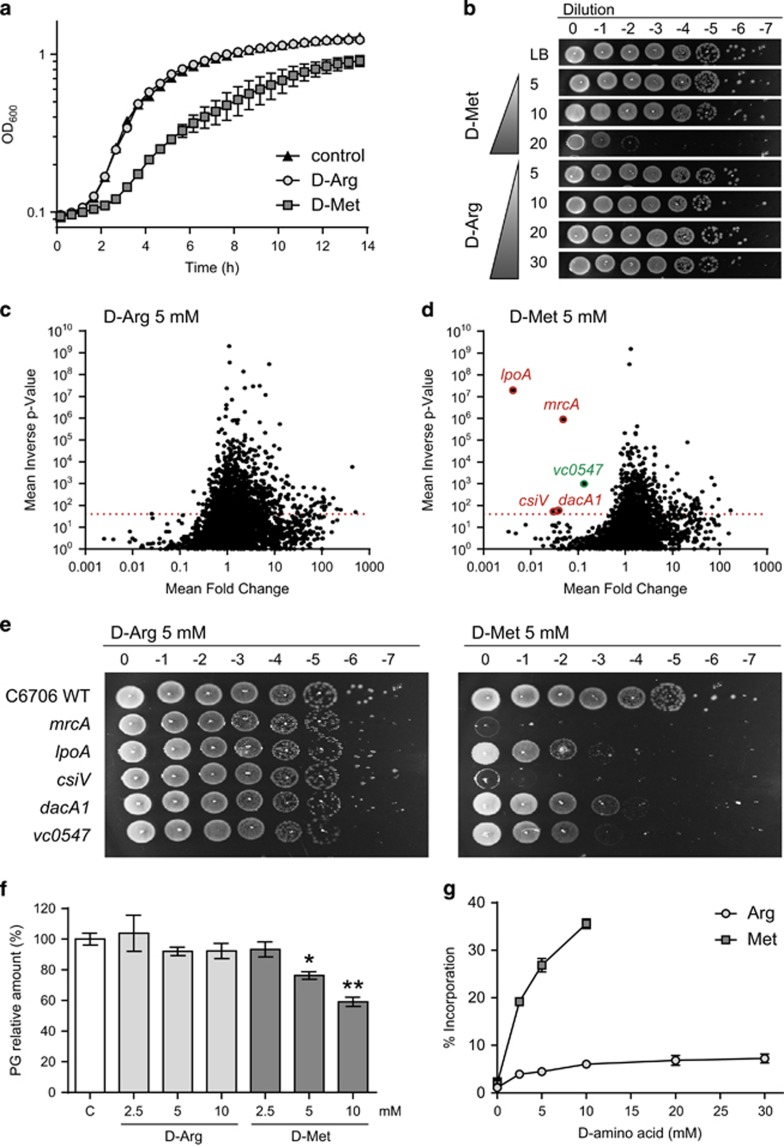
Figure 2.
D-arginine does not regulate cell wall synthesis in V. cholerae. (a) Growth curves of wild-type V. cholerae in LB in the absence (control) and presence of 20 mm D-Arg or D-Met. (b) Growth of wild-type V. cholerae on D-amino acid containing plates. Serial dilutions were spotted onto LB plates containing 5–30 mm D-Arg or D-Met. (c, d) Volcano plots depicting the ratio of read counts mapped to individual genes in transposon libraries of V. cholerae plated onto 5 mm D-Arg (c) or D-Met (d) plates compared with control libraries plated onto LB agar without D-amino acid. Genes shown in red (cell wall-associated proteins) and green (amino acid biosynthesis protein) are considered significantly underrepresented. (e) Validation of plating defects of selected V. cholerae mutants identified in the transposon screen. Serial dilutions were spotted onto LB plates supplemented with 5 mm D-Arg or D-Met. (f) Peptidoglycan quantification in D-Arg and D-Met supplemented V. cholerae cultures. Peptidoglycan relative amount (%) is normalized to the wild-type in LB control media. P-value <0.05 (*). P-value <0.01 (**). (g) D-amino acid incorporation into the cell wall of V. cholerae upon addition of different concentrations of D-Arg or D-Met. Relative abundance (%) of D-Arg or D-Met modified muropeptides is represented.