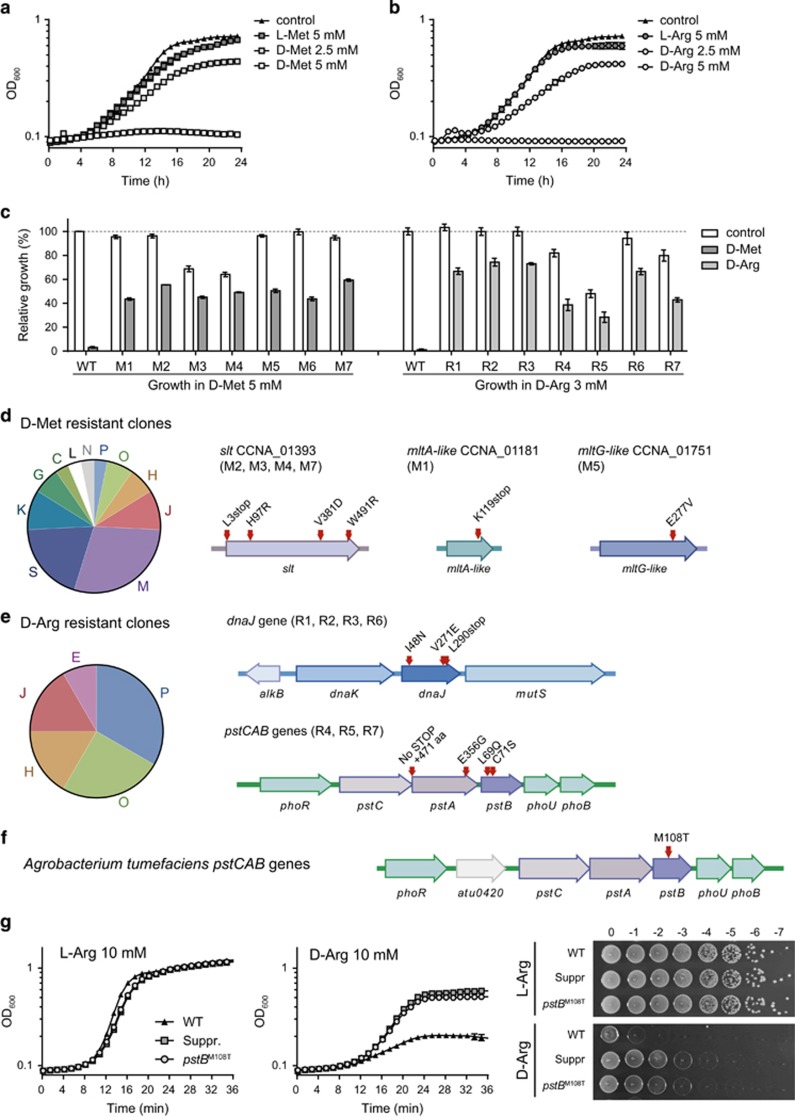
Figure 4.
Mutations in the Pi uptake and protein folding systems suppress D-arginine lethality in sensitive bacteria. (a, b) Growth curves of wild-type C. crescentus in PYE in the absence (control) and presence of 2.5 or 5 mm D-Met (a) or D-Arg (b). (c) Relative growth of C. crescentus suppressor mutants isolated from D-Met containing plates (left, M1–M7) and from D-Arg containing plates (right, R1-R7). Bacteria were grown in PYE media without D-amino acid (control, white bars) or supplemented with 5 mm D-Met (dark gray bars) or 3 mm D-Arg (light gray bars). (d) COG classification of the mutations found in the genomes of D-Met-resistant derivatives of C. crescentus. Mutations conferring resistance to D-Met map to the lytic transglycosylases slt (CCNA_01393), mltA-like (CCNA_01181) and mltG-like (CCNA_01751) genes. (e) COG classification of the mutations found in the genomes of D-Arg-resistant derivatives of C. crescentus. Mutations conferring resistance to D-Arg mapped to the dnaJ gene (CCNA_00011) or the pstCAB operon (CCNA_00292-00294. (f) Suppressor mutation of pstB gene (atu0423) in a D-Arg-resistant A. tumefaciens derivative. (g) A. tumefaciens growth defect in the presence of 10 mm D-Arg is alleviated by a point mutation in PstB (pstBM108T) both in liquid and solid media. COG groups: P: inorganic ion transport and metabolism; O: post-translational modification, protein turnover, chaperone functions; H: coenzyme metabolism and transport; J: translation; E: amino acid metabolism and transport; M: cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; S: unknown function; K: transcription; G: carbohydrate metabolism and transport; C: energy production and conversion; L: replication and repair; N: cell motility.