Table 1.
HIV-1 and HBV Activity of Conjugates 1–5b, 6, and 7 Compared to TFV and TDFa
| HIV-l
|
HBV
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ident. | Structure | EC50b (PBMCs) | CC50b(PBMCs) | TI (CC50/EC50) | EC50b (HepG2) | CC50b (HepG2) | TI (CC50/EC50) |
|
|
|
||||||
| TFV |
|
0.320 | > 100 | >300 | – | – | – |
| TDF |
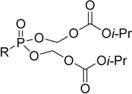
|
0.0045 | 44.0 | 9500 | 0.34 | 64.5 | 190 |
| 1b |
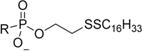
|
0.00065 | 14.3 | 22000 | 0.020 | >25 | > 1200 |
| 2b |
|
< 0.0005 | >50 | >100000 | 0.248 | >50 | >200 |
| 3b |
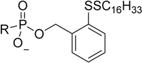
|
0.0229 | 17.2 | 751 | 4.48 | 17.5 | 3.9 |
| 4b |
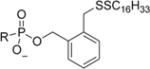
|
< 0.0005 | 15.9 | >31800 | 0.152 | 32.5 | 214 |
| 5b |
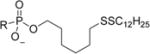
|
0.007 | >50 | >7000 | 1.05 | >50 | >47 |
| 6 |
|
18.6 | > 100 | >5.38 | 41.9 | >100 | >2 |
| 7 |
|
5.13 | > 100 | > 18 | > 100 | > 100 | > 1 |
All data represent an average of triplicate experiments. R = tenofovir.
EC50, effective concentration (in μM) required to inhibit HIV-1 or HBV by 50%.
CC50, effective concentration (in μM) required to reduce the viability of uninfected cells by 50%.
