Fig. 5.
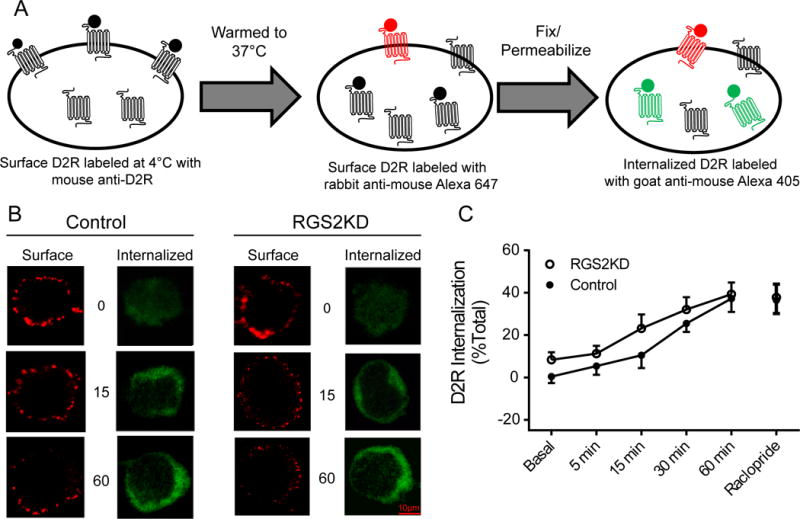
RGS2 knockdown slightly enhances constitutive D2R internalization. (A) A schematic diagram of surface and intracellular D2R labeling for measurement of constitutive D2R internalization. Surface D2Rs were saturated with mouse anti-D2R. Then cells were warmed to 37°C to allow constitutive internalization for the indicated time points. At the end of each time point, remaining primary antibody-bound surface D2Rs that did not internalize were labeled with goat anti-mouse Alexa 647 (red). D2Rs that were internalized were identified by labeling with goat anti-mouse Alexa 405 (blue, pseudo-colored to green). (B) Representative confocal images of surface and internalized D2Rs in control and RGS2 knockdown (RGS2KD) cells. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of constitutive D2R internalization. Internalized D2Rs were represented as percent of total D2Rs. Constitutive internalization occurred in a time-dependent manner in both control and RGS2 knockdown cells (P<0.01, a two-way ANOVA, n=55-70 cells/group). RGS2 knockdown produced a small but significant overall increase in constitutive D2R internalization when compared to control cells. Pre-treatment with raclopride (1μM, 30 min) did not inhibit constitutive D2R internalization. Experiments were replicated three times. Data are expressed as relative to the vehicle treatment in the control cells.
