Fig. 1.
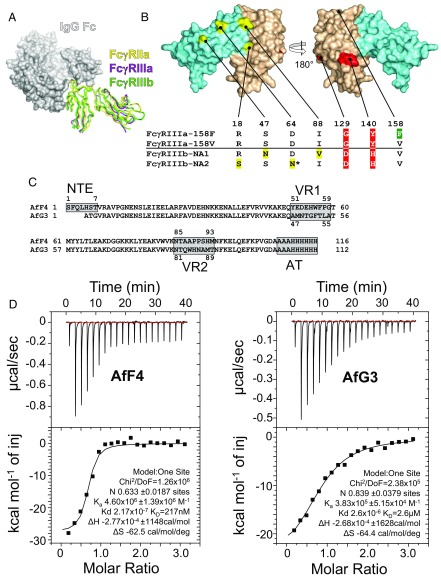
The challenge of structural homology and the selection of specific protein-based inhibitors of FcγRIIIa. (A) Superimposed crystal structures of three FcγR ectodomains are shown as ribbon diagrams in complex with a space-filling model of the Fc domain of IgG1. FcγRIIa (PDB ID code 3RY6) is shown in yellow, FcγRIIIa (PDB ID code 3AY4) is shown in purple, and FcγRIIIb (PDB ID code 1T83) is shown in green. (B) Structural homology between FcγRIIIa and FcγRIIIb. The four amino acids in yellow differ in the FcγRIIIb NA1 and NA2 allotypes; the two amino acids in red discriminate FcγRIIIa from FcγRIIIb; and the location of the FcγRIIIa-158F/V allotype is green. The FcγRIIIb-NA2 allotype has an extra N-linked glycosylation site at Asn64. Extracellular domains 1 and 2 are depicted in aquamarine (D1 residues 1–89) and wheat (D2 residues 90–174), respectively. (C) The aligned amino acid sequences of AfF4 and AfG3 highlighting the positions of VR1, VR2, and the affinity tag (AT). Note that AfF4 has an additional NTE. Residue numbering within the VRs is indicated. (D) ITC of the FcγRIIIa–AfF4 and –AfG3 interactions with isotherms and data fits. FcγRIIIa was at 10 µM in the sample cell, and Affimer proteins were injected in stepwise additions of 2 μL to a final concentration of 100 µM.