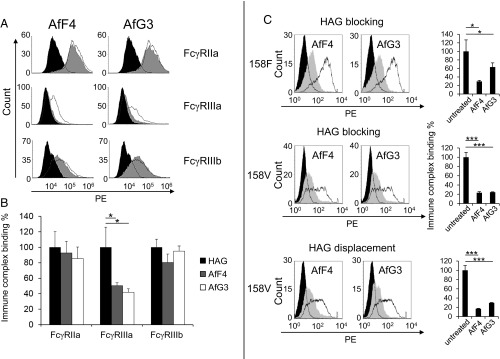
Fig. 2.
Affimer proteins AfF4 and AfG3 specifically reduce immune complex binding to FcγRIIIa. Heat-aggregated HAG-binding assays utilized HEK293 cells stably expressing the full-length Fcγ receptors. Cells were treated with each Affimer protein before the addition of HAG followed by anti-human F(ab′)2 fragments labeled with phycoerythrin (PE); binding was measured by flow cytometry. (A, Top Row) Representative examples of the effect of AfF4 and AfG3 on immune complex (HAG) binding on cells expressing FcγRIIa; the unfilled distribution represents the untreated cells, and the gray distribution represents binding to cells pretreated with Affimer protein. The filled black region represents background binding of F(ab′)2 fragments to the cells. (Middle Row) Both Affimer proteins reduce HAG binding to cells expressing FcγRIIIa alone. (Bottom Row) Affimer proteins had little effect on HAG binding to cells expressing FcγRIIIb. (B) Histograms showing the reproducibility of AfF4 and AfG3 inhibition of HAG binding to FcγRs expressed stably on HEK293 cells. Values are normalized to Affimer proteins-untreated (HAG only) measurements. Error bars indicate the SD within three biological replicates. (C, Top and Middle) Representative experiments that demonstrate both Affimer proteins (AfF4 and AfG3) reduce the binding of heat-aggregated IgG1 to both common allotypes of FcγRIIIa, -158F and -158V. The open black histograms show the binding of HAG to cells expressing FcγRIIIa. The effect of preloading the receptors with Affimer proteins for 1 h before adding HAG is shown as a solid gray histogram. The filled black histograms are controls without HAG. (Bottom) Both Affimer proteins displaced HAG from the 158V allotype when added after HAG. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t test.