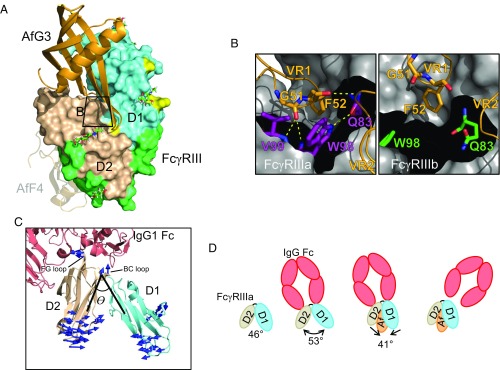
Fig. 4.
Molecular basis of AfG3 selectivity for FcγRIIIa. (A) Overview of the binding position of AfG3 (orange cartoon) to FcγRIII (D1 in aquamarine, D2 in wheat, IgG contacts in light green, polymorphic residues in yellow, FcγRIIIa discriminatory residues in red). N-linked glycans with distinguishable electron density in the crystal structures are depicted as sticks and listed in Table S6. The zoomed window for B is indicated by the black box. The AfF4-binding position is depicted as a transparent cartoon to aid comparison. (B) MD simulation snapshot of the interaction of AfG3 with FcγRIIIa (purple sticks) and FcγRIIIb (green sticks). γa-Trp98 intercalates between AfG3 VR1 and VR2, resulting in several stable intermolecular H-bonds, whereas these contacts did not form in the MD simulations in FcγRIIIb. (C) Cartoon representation of FcγRIIIa (aquamarine and wheat) interacting with IgG Fc (salmon). The interdomain angle θ is described by lines connecting the [CA] of γa-Trp90 at the top of the hinge and the [CA] of Asn169 in D2 and the [CA] of Gln83 in D1. Mode vectors describing the allosteric change from the IgG-bound state to the AfG3-bound state are shown as blue arrows. Mode vectors shorter than 3 Å are not shown. (D) Schematic representation of the allosteric change induced by AfG3. Unbound FcγRIII (PDB ID code 1FNL) describes a D1–D2 interdomain angle θ of 46°, which opens to 53° on interaction with IgG Fc. FcγRIIIa interaction with AfG3 narrows the D1–D2 angle by 12° to 41°, and we hypothesize that this allosteric shift causes sufficient deformation of the IgG Fc binding site to induce IgG Fc displacement.