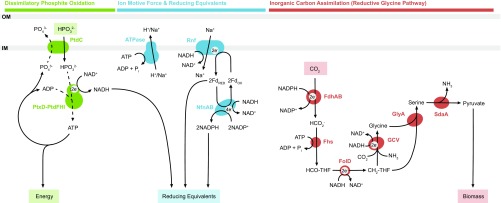
Fig. 6.
Genomics-based metabolic model of dissimilatory phosphite oxidation coupled to CO2 reduction in Ca. Phosphitivorax anaerolimi Phox-21. Dotted lines denote putative mechanisms based on physiological and genomic observations that have yet to be confirmed by direct biochemical evidence. Dissimilatory phosphite oxidation proteins: PtdC, phosphite transporter; PtdF, nucleoside-diphosphate-sugar epimerase; PtdH, radical SAM superfamily enzyme; PtdI, hypothetical protein; PtxD, phosphite dehydrogenase. Ion motive force and reducing equivalents proteins: ATPase, ATP synthase complex; NfnAB, NAD-dependent ferredoxin:NADP oxidoreductase; Rnf, sodium-translocating ferredoxin:NAD oxidoreductase complex. Inorganic carbon assimilation (reductive glycine pathway) proteins: FdhAB, NADP-dependent formate dehydrogenase; Fhs, formate:THF ligase; FolD, methenyl-THF cyclohydrolase/methylene-THF dehydrogenase; GCV, glycine cleavage system (GcvH, lipoate-binding protein; GcvP, glycine dehydrogenase; GcvT, aminomethyltransferase; Lpd, dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase); GlyA, serine hydroxymethyltransferase; SdaA, serine deaminase.