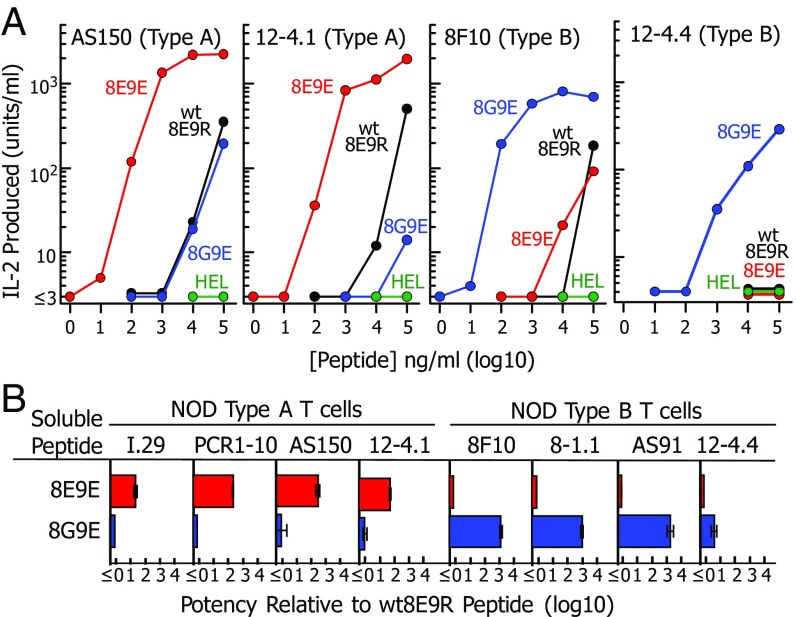
Fig. 2.
Mutations to the B:12–22 peptide create reciprocal superagonists for type A vs. type B insulin-reactive T cells. (A) Various concentrations of soluble WT8E9R (black), 8E9E (red), and 8G9E (blue) peptides (Fig. 1B) were presented by fixed M12.C3-IAg7 cells to two NOD mouse type A and two type B insulin-reactive T cells (Table S1). Results of a single experiment are presented as IL-2 produced after 24 h vs. the concentration of the offered peptide. The HEL peptide was used as a negative control (green). (B) Peptide titration experiments were performed as in A with all eight NOD mouse T cells listed in Table S1. The titration data were fitted with parallel third-order polynominal curves. The peptide potency was defined as the shift in the titration curve relative to that of the WT8E9R peptide. Results are shown as the geometric average and SEM of three separate experiments.